Molecular networks in Network Medicine: Development and applications
- PMID: 32307915
- PMCID: PMC7955589
- DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.1489
Molecular networks in Network Medicine: Development and applications
Abstract
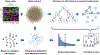
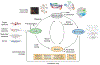
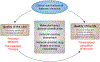
Network Medicine applies network science approaches to investigate disease pathogenesis. Many different analytical methods have been used to infer relevant molecular networks, including protein-protein interaction networks, correlation-based networks, gene regulatory networks, and Bayesian networks. Network Medicine applies these integrated approaches to Omics Big Data (including genetics, epigenetics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, and proteomics) using computational biology tools and, thereby, has the potential to provide improvements in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of complex diseases. We discuss briefly the types of molecular data that are used in molecular network analyses, survey the analytical methods for inferring molecular networks, and review efforts to validate and visualize molecular networks. Successful applications of molecular network analysis have been reported in pulmonary arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, chronic lung diseases, and drug development. Important knowledge gaps in Network Medicine include incompleteness of the molecular interactome, challenges in identifying key genes within genetic association regions, and limited applications to human diseases. This article is categorized under: Models of Systems Properties and Processes > Mechanistic Models Translational, Genomic, and Systems Medicine > Translational Medicine Analytical and Computational Methods > Analytical Methods Analytical and Computational Methods > Computational Methods.
Keywords: big data; molecular networks; network medicine.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
Edwin K. Silverman: Grant support from GSK and Bayer
Harald H.H.W. Schmidt: None reported
Eleni Anastasiadou: None reported
Lucia Altucci: None reported
Marco Angelini: None reported
Lina Badimon: None reported
Jean-Luc Balligand: None reported
Giuditta Benincasa: None reported
Giovambattista Capasso: None reported
Federica Conte: None reported
Antonella Di Costanzo: None reported
Lorenzo Farina: None reported
Giulia Fiscon: None reported
Laurent Gatto: None reported
Michele Gentili: None reported
Joseph Loscalzo: Scipher Medicine, Inc.—cofounder of this biotech start-up, uses network medicine strategies to define biomarkers of therapeutic efficacy and to repurpose drugs
Cinzia Marchese: None reported
Claudio Napoli: None reported
Paola Paci: None reported
Manuela Petti: None reported
John Quackenbush: None reported
Paolo Tieri: None reported
Davide Viggiano: None reported
Gemma Vilahur: None reported
Kimberly Glass: None reported
Jan Baumbach: None reported
Figures


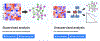
References
-
- Alkorta-Aranburu G, Carmody D, Cheng YW, Nelakuditi V, Ma L, Dickens JT, … Del Gaudio D (2014). Phenotypic heterogeneity in monogenic diabetes: the clinical and diagnostic utility of a gene panel-based next-generation sequencing approach. Mol Genet Metab, 113(4), 315–320. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.09.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P01HL105339/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL114501/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133135/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50GM107618/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM107618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K25HL133599/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL137927/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL089856/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HG007690/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL147148/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007690/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL133599/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147148/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL119145/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA220523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL105339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

