HRD1 prevents atherosclerosis-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis by promoting LOX-1 degradation
- PMID: 32308114
- PMCID: PMC7469520
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1754561
HRD1 prevents atherosclerosis-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis by promoting LOX-1 degradation
Abstract
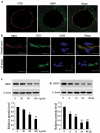
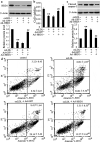
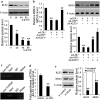
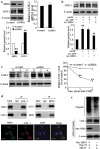
The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl reductase degradation (HRD1) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that can preserve heart structure and function, but its role in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis (AS) is unclear. The aim of this study was to explore the role and biological function of HRD1 in AS. HRD1 expression was significantly decreased in atherosclerotic intima and ox-LDL led to a decrease of HRD1 level in endothelial cells (ECs). Forced expression of HRD1 inhibited the endothelial apoptosis induced by ox-LDL. The transcription factor KLF2 specifically bound to the HRD1 promoter and positively regulated HRD1 expression. KLF2 up-regulation could reverse the decrease of HRD1 level in ECs treated with ox-LDL. Further analysis showed that HRD1 interacted with LOX-1 and promoted ubiquitination and degradation of LOX-1 by the proteasome. Deletion of LOX-1 attenuated the ECs apoptosis induced by HRD1 downregulation. Pravastatin, which protected EC from damage via a KLF2-dependent mechanism, could dose-dependently enhanced HRD1 expression in EC exposed to ox-LDL. Interestingly, interference of HRD1 abolished the cytoprotective effect of pravastatin. Collectively, our data indicate that decreased HRD1 expression leads to apoptosis of ECs and restoration of HRD1 expression could represent a novel strategy for human AS therapy.
Keywords: HRD1; LOX-1; apoptosis; atherosclerosis; endothelial cell.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fluid shear stress regulates the expression of Lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 via KLF2-AP-1 pathway depending on its intensity and pattern in endothelial cells.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Mar;270:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.01.038. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 29407891
-
The protective effects of aloperine against ox-LDL-induced endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in HUVECs.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;48(1):107-115. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1699816. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31852304
-
Azilsartan ameliorates ox-LDL-induced endothelial dysfunction via promoting the expression of KLF2.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 4;13(9):12996-13005. doi: 10.18632/aging.202973. Epub 2021 May 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33946046 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized LDL, LOX-1 and atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011 Oct;25(5):419-29. doi: 10.1007/s10557-011-6341-5. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011. PMID: 21947818 Review.
-
Role of Ox-LDL and LOX-1 in Atherogenesis.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(9):1693-1700. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180508100950. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29737246 Review.
Cited by
-
USF1 transcriptionally activates USP14 to drive atherosclerosis by promoting EndMT through NLRC5/Smad2/3 axis.Mol Med. 2024 Feb 29;30(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00798-8. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38424494 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress-Mediated Programmed Cell Death: a Potential Therapy Target for Atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Aug;38(4):819-832. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07414-z. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 36522550 Review.
-
New Dawn for Atherosclerosis: Vascular Endothelial Cell Senescence and Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 13;24(20):15160. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015160. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 (LOX-1): A Potential Therapeutic Target in Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Aug;16(4):1412-1423. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01307-z. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39576412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Casting Light on the Janus-Faced HMG-CoA Reductase Degradation Protein 1: A Comprehensive Review of Its Dualistic Impact on Apoptosis in Various Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6842-6863. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03994-z. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38356096 Review.
References
-
- Mäkinen PI, Ylä-Herttuala S.. Therapeutic gene targeting approaches for the treatment of dyslipidemias and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2013;24:116–122. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins PN. Molecular biology of atherosclerosis. Physiol Rev. 2013;93:1317–1542. - PubMed
-
- Meyers MR, Gokce N. Endothelial dysfunction in obesity: etiological role in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2007;14:365–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
