Estimation of YKL-40 Levels in Serum and Gingival Crevicular Fluid in Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Patients among South Indian Population: A Clinical Study
- PMID: 32308295
- PMCID: PMC7145233
- DOI: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_629_18
Estimation of YKL-40 Levels in Serum and Gingival Crevicular Fluid in Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Patients among South Indian Population: A Clinical Study
Abstract
Background: YKL-40 is a novel potential inflammatory marker in relation to both acute and chronic inflammation. It is secreted by activated neutrophils and macrophages in acute or chronic inflammation. It strongly binds to chitin and heparin. There remains paucity in information regarding the quantification of YKL-40 levels in serum and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in patients with periodontal disease.
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate and estimate the YKL-40 levels in serum and GCF samples collected from patients with or without periodontitis and type 2 diabetes among the South Indian population.
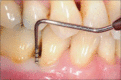
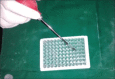
Materials and methods: A total of 40 patients were included who were divided into four groups based on inclusion and exclusion criteria as follows: Group A comprised ten healthy individuals, Group B comprised ten patients diagnosed with chronic periodontitis without type 2 diabetes, Group C comprised ten patients diagnosed with chronic periodontitis with type 2 diabetes, and Group D comprised ten patients diagnosed with only type 2 diabetes. Gingival Index (GI), pocket depth (PD), and clinical attachment level (CAL) were recorded at baseline. Serum and GCF samples were collected at baseline which were subjected to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis for estimation of YKL-40 levels.
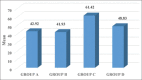
Results: All the clinical parameters (GI, PD, and CAL) and the concentration of YKL-40 level in serum and GCF samples were statistically significant among the groups. The amount of YKL-40 in GCF and serum was found to be highly correlated with PD of patients in all the groups.
Conclusions: Within the limitations of the sample size, the present study indicates that the measurement of YKL-40 in Serum and GCF samples shows potential as a quantitative indicator of periodontal disease extent.
Keywords: Acute-phase protein; YKL-40; chronic periodontitis; diabetes; gingival crevicular fluid; serum.
Copyright: © 2020 Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
YKL-40 level in gingival crevicular fluid from patients with periodontitis and type 2 diabetes.Oral Dis. 2015 Jul;21(5):667-73. doi: 10.1111/odi.12334. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Oral Dis. 2015. PMID: 25740558
-
Analysis of YKL-40 acute-phase protein and interleukin-6 levels in periodontal disease.J Periodontol. 2014 Sep;85(9):1240-6. doi: 10.1902/jop.2014.130631. Epub 2014 Mar 17. J Periodontol. 2014. PMID: 24635545
-
Effect of scaling and root planing on gingival crevicular fluid level of YKL-40 acute phase protein in chronic periodontitis patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A clinico-biochemical study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018 Jan-Feb;22(1):40-44. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_95_17. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018. PMID: 29568171 Free PMC article.
-
Nonsurgical Periodontal Therapy Reduces Salivary and Gingival Crevicular Fluid YKL-40 and IL-6 Levels in Chronic Periodontitis.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020 Sep 4;18(4):815-822. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a45086. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2020. PMID: 32895666 Free PMC article.
-
Gingival crevicular fluid alkaline phosphatase levels in postmenopausal women: effects of phase I periodontal treatment.J Periodontol. 2006 Jan;77(1):67-72. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.77.1.67. J Periodontol. 2006. PMID: 16579705
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Effects and Regulatory Mechanisms of Chitinase-3-like-1 in Multiple Human Body Systems: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 15;25(24):13437. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413437. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous and microbial biomarkers for periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 5;14:1292596. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1292596. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38149100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF): A Diagnostic Tool for the Detection of Periodontal Health and Diseases.Molecules. 2021 Feb 24;26(5):1208. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051208. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Initial Periodontal Therapy on Heat Shock Protein 70 Levels in Gingival Crevicular Fluid from Periodontitis Patients.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 24;9(10):3072. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103072. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32987652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keles ZP, Keles GC, Avci B, Cetinkaya BO, Emingil G. Analysis of YKL-40 acute-phase protein and interleukin-6 levels in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2014;85:1240–6. - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, et al. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: A consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: A consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the study of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:193–203. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;69:89–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
