Add-on pegylated interferon augments hepatitis B surface antigen clearance vs continuous nucleos(t)ide analog monotherapy in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis B surface antigen ≤ 1500 IU/mL: An observational study
- PMID: 32308352
- PMCID: PMC7152523
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i13.1525
Add-on pegylated interferon augments hepatitis B surface antigen clearance vs continuous nucleos(t)ide analog monotherapy in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis B surface antigen ≤ 1500 IU/mL: An observational study
Abstract
Background: Nucleos(t)ide analog (NA) has shown limited effectiveness against hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) clearance in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients.
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of add-on peginterferon α-2a (peg-IFN α-2a) to an ongoing NA regimen in CHB patients.
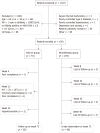
Methods: In this observational study, 195 CHB patients with HBsAg ≤ 1500 IU/mL, hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-negative (including HBeAg-negative patients or HBeAg-positive patients who achieved HBeAg-negative after antiviral treatment with NA) and hepatitis B virus-deoxyribonucleic acid < 1.0 × 102 IU/mL after over 1 year of NA therapy were enrolled between November 2015 and December 2018 at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, China. Patients were given the choice between receiving either peg-IFN α-2a add-on therapy to an ongoing NA regimen (add-on group, n = 91) or continuous NA monotherapy (monotherapy group, n = 104) after being informed of the benefits and risks of the peg-IFN α-2a therapy. Total therapy duration of peg-IFN α-2a was 48 wk. All patients were followed-up to week 72 (24 wk after discontinuation of peg-IFN α-2a). The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with HBsAg clearance at week 72.
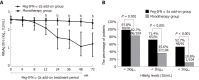
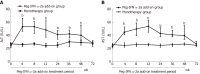
Results: Demographic and baseline characteristics were comparable between the two groups. Intention-to-treatment analysis showed that the HBsAg clearance rate in the add-on group and monotherapy group was 37.4% (34/91) and 1.9% (2/104) at week 72, respectively. The HBsAg seroconversion rate in the add-on group was 29.7% (27/91) at week 72, and no patient in the monotherapy group achieved HBsAg seroconversion at week 72. The HBsAg clearance and seroconversion rates in the add-on group were significantly higher than in the monotherapy group at week 72 (P < 0.001). Younger patients, lower baseline HBsAg concentration, lower HBsAg concentrations at weeks 12 and 24, greater HBsAg decline from baseline to weeks 12 and 24 and the alanine aminotransferase ≥ 2 × upper limit of normal during the first 12 wk of therapy were strong predictors of HBsAg clearance in patients with peg-IFN α-2a add-on treatment. Regarding the safety of the treatment, 4.4% (4/91) of patients in the add-on group discontinued peg-IFN α-2a due to adverse events. No severe adverse events were noted.
Conclusion: Peg-IFN α-2a as an add-on therapy augments HBsAg clearance in HBeAg-negative CHB patients with HBsAg ≤ 1500 IU/mL after over 1 year of NA therapy.
Keywords: Add-on therapy; Chronic hepatitis B; Hepatitis B surface antigen clearance; Hepatitis B surface antigen seroconversion; Nucleos(t)ide analog; Peginterferon α-2a.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors do not have any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu.; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017;67:370–398. - PubMed
-
- Chang TT, Lai CL, Kew Yoon S, Lee SS, Coelho HS, Carrilho FJ, Poordad F, Halota W, Horsmans Y, Tsai N, Zhang H, Tenney DJ, Tamez R, Iloeje U. Entecavir treatment for up to 5 years in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;51:422–430. - PubMed
-
- Lau GK, Piratvisuth T, Luo KX, Marcellin P, Thongsawat S, Cooksley G, Gane E, Fried MW, Chow WC, Paik SW, Chang WY, Berg T, Flisiak R, McCloud P, Pluck N Peginterferon Alfa-2a HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B Study Group. Peginterferon Alfa-2a, lamivudine, and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2682–2695. - PubMed
-
- Janssen HL, van Zonneveld M, Senturk H, Zeuzem S, Akarca US, Cakaloglu Y, Simon C, So TM, Gerken G, de Man RA, Niesters HG, Zondervan P, Hansen B, Schalm SW HBV 99-01 Study Group; Rotterdam Foundation for Liver Research. Pegylated interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365:123–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

