Effect of Aqueous Extract and Polyphenol Fraction Derived from Thymus atlanticus Leaves on Acute Hyperlipidemia in the Syrian Golden Hamsters
- PMID: 32308705
- PMCID: PMC7142347
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3282596
Effect of Aqueous Extract and Polyphenol Fraction Derived from Thymus atlanticus Leaves on Acute Hyperlipidemia in the Syrian Golden Hamsters
Abstract
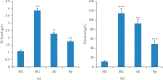
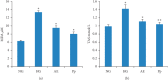
Thymus atlanticus, an endemic plant of Morocco, is traditionally used as a liniment or a drink to treat various diseases. However, there are few available scientific data regarding its biological effects. In this connection, the present study aimed to investigate the hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of aqueous extract and polyphenol fraction of Thymus atlanticus in Syrian golden hamsters treated with Triton WR-1339 (triton, 20 mg/100 g body weight). The hamsters orally received the extracts (400 mg/kg), and blood samples were collected after 24 h of treatment to determine plasma lipid, insulin, and fasting blood glucose levels. Plasma malondialdehyde level and plasma total antioxidant (TAS) were also evaluated. The T. atlanticus extracts significantly decreased triglycerides, total cholesterol, VLDL-C, and LDL-C and increased HDL-C when compared with the hyperlipidemic group. Both extracts suppressed the effect of the triton injection on TAS and reduced the level of plasma malondialdehyde. The extracts produced no significant change in the blood glucose level but effectively prevented the mild hyperinsulinemia induced by triton. These findings suggest that T. atlanticus may be a useful alternative treatment for the control of hyperlipidemia and its related diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Mhamed Ramchoun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
-
- Saeed A., Feofanova E., Yu B., et al. Association of elevated triglycerides and atherogenic lipoproteins with incident cardiovascular diseases: insights from genetic data in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Journal of Clinical Lipidology. 2017;11(3):p. 788. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2017.04.028. - DOI
-
- WHO. Raised Cholesterol. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2015.
-
- Sultan S., D’Souza A., Zabetakis I., et al. The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier; 2019. Statins: rationale, mode of action, and side effects; pp. 171–200.
-
- Ramchoun M., Harnafi H., Alem C., et al. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effect of polyphenol-rich extracts from Moroccan thyme varieties. e-SPEN Journal. 2012;7(3):e119–e124. doi: 10.1016/j.clnme.2012.02.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

