Predicting Adverse Drug Reactions on Distributed Health Data using Federated Learning
- PMID: 32308824
- PMCID: PMC7153050
Predicting Adverse Drug Reactions on Distributed Health Data using Federated Learning
Abstract
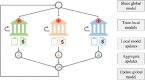
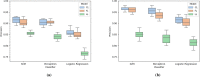
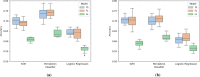
Using electronic health data to predict adverse drug reaction (ADR) incurs practical challenges, such as lack of adequate data from any single site for rare ADR detection, resource constraints on integrating data from multiple sources, and privacy concerns with creating a centralized database from person-specific, sensitive data. We introduce a federated learning framework that can learn a global ADR prediction model from distributed health data held locally at different sites. We propose two novel methods of local model aggregation to improve the predictive capability of the global model. Through comprehensive experimental evaluation using real-world health data from 1 million patients, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach in achieving comparable performance to centralized learning and outperforming localized learning models for two types of ADRs. We also demonstrate that, for varying data distributions, our aggregation methods outperform state-of-the-art techniques, in terms of precision, recall, and accuracy.
©2019 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Jensen Peter B, Jensen Lars J, Brunak SoÃÿren. Mining electronic health records: Towards better research applications and clinical care. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2012;13:395–405. - PubMed
-
- Madigan David, Ryan Patrick B, Schuemie Martijn, Stang Paul E, Overhage J Marc, Hartzema Abraham G, Suchard Marc A, DuMouchel William, Jesse A Berlin. Evaluating the impact of database heterogeneity on observational study results. American journal of epidemiology. 2013;178(4):645–651. - PMC - PubMed
-
- FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS). 2019 Feb; https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/ucm135151.htm Accessed:
-
- The Sentinel Initiative. 2019 Feb; https://www.sentinelinitiative.org/ Accessed:
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
