A High Recall Classifier for Selecting Articles for MEDLINE Indexing
- PMID: 32308868
- PMCID: PMC7153058
A High Recall Classifier for Selecting Articles for MEDLINE Indexing
Abstract
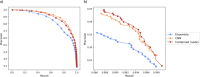
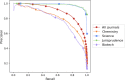
MEDLINE is the National Library of Medicine's premier bibliographic database for biomedical literature. A highly valuable feature of the database is that each record is manually indexed with a controlled vocabulary called MeSH. Most MEDLINE journals are indexed cover-to-cover, but there are about 200 selectively indexed journals for which only articles related to biomedicine and life sciences are indexed. In recent years, the selection process has become an increasing burden for indexing staff, and this paper presents a machine learning based system that offers very significant time savings by semi-automating the task. At the core of the system is a high recall classifier for the identification of journal articles that are in-scope for MEDLINE. The system is shown to reduce the number of articles requiring manual review by 54%, equivalent to approximately 40,000 articles per year.
©2019 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- MEDLINE/PubMed baseline; 2018. Available from: https://mbr.nlm.nih.gov/Download/ Baselines/2018/
-
- Cohen AM, Hersh WR. The TREC 2004 genomics track categorization task: classifying full text biomedical documents. Journal of Biomedical Discovery and Collaboration. 2006 Mar;1(1):4 Available from: https: //doi.org/10.1186/1747-5333-1-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wiegers TC, Davis AP, Mattingly CJ. Collaborative biocuration - text-mining development task for document prioritization for curation. Database. 2012 Nov;2012. Available from: https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ database/bas037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Del Fiol G, Michelson M, Iorio A, Cotoi C, Haynes RB. A deep learning method to automatically identify reports of scientifically rigorous clinical research from the biomedical literature comparative analytic study. J Med Internet Res. 2018 Jun;20(6):e10281. Available from: http://www.jmir.org/2018/6/e10281/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
