Techniques of Eyebrow Lifting: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 32308957
- PMCID: PMC7151508
- DOI: 10.18502/jovr.v15i2.6740
Techniques of Eyebrow Lifting: A Narrative Review
Abstract
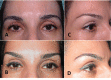
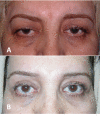
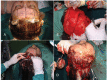
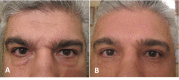
None of brow lift techniques are completely satisfactory because of their limited effectiveness, lack of longevity, and potential complications. The aim of this study was to provide a comprehensive review of the literature on the pros and cons of the most popular techniques in brow and forehead lift. Relevant original articles in the PubMed database (English language) were sought using the search terms "eyebrow lift", "forehead lift", "periorbital rejuvenation", "eyebrow ptosis", "blepharoplasty and eyebrow change", "surgical eyebrow lift", and "non-surgical eyebrow lift", No date limitation was considered. Titles and abstracts were scanned to include the most pertinent articles. Subsequently, full texts of included articles (111 articles) were skimmed and finally 56 references were selected for the review. A narrative synthesis of data was finally undertaken with particular attention to the indications, techniques, and common complications of the eyebrow lift procedures. Ten popular techniques including two non-surgical methods (Botulinum toxin A and soft tissue fillers) were reviewed in this article. In general, non-surgical methods of forehead/brow lift are temporary, need less experience and correction would be easier should any complication occur. Surgical methods are divided into three categories: trans-blepharoplasty eyebrow lift, direct eyebrow lift, and trans-forehead eyebrow/forehead lift. Currently, the most popular method is the endoscopic forehead lift approach even though its longevity is limited. Direct brow-lift is particularly useful in patients with facial palsy and those who are more likely to be accepting of the scar (male gender, high forehead hair line).
Keywords: Endoscopy; Esthetics; Eyebrow; Forehead; Lifting; Rejuvenation; Blepharoplasty.
Copyright © 2020 Karimi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
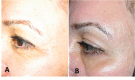
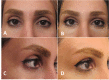

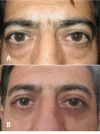
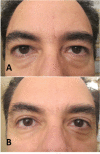


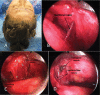
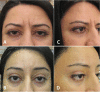
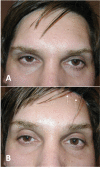
References
-
- Kashkouli Mohsen Bahmani, Abolfathzadeh Navid, Abdolalizadeh Parya, Sianati Hamed, Karimi Nasser. Upper blepharoplasty and eyebrow position. Expert Review of Ophthalmology. 2017;12(3):251–259. doi: 10.1080/17469899.2017.1311207. - DOI
-
- Kashkouli Mohsen Bahmani, Abdolalizadeh Parya, Abolfathzadeh Navid, Sianati Hamed, Sharepour Maria, Hadi Yasaman. Corrigendum to “Periorbital facial rejuvenation; applied anatomy and pre-operative assessment” [J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 29 (3), (September 2017) 154–168] Journal of Current Ophthalmology. 2018;30(2):188–189. doi: 10.1016/j.joco.2017.11.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
