In Vivo Cognitive-Enhancing, Ex Vivo Malondialdehyde-Lowering Activities and Phytochemical Profiles of Aqueous and Methanolic Stem Bark Extracts of Piliostigma thonningii (Schum.)
- PMID: 32308992
- PMCID: PMC7128055
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1367075
In Vivo Cognitive-Enhancing, Ex Vivo Malondialdehyde-Lowering Activities and Phytochemical Profiles of Aqueous and Methanolic Stem Bark Extracts of Piliostigma thonningii (Schum.)
Abstract
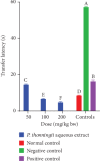
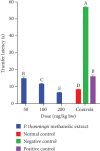
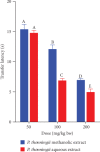
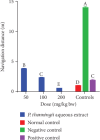
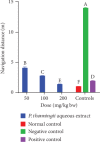
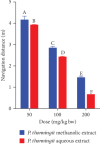
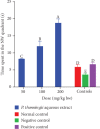
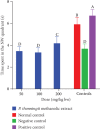
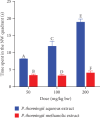
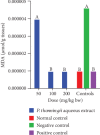
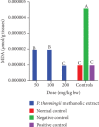
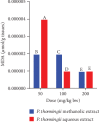
Cognitive impairment (CI) is among the leading causes of disability in humans. It is estimated that over 35.6 million people are suffering from Alzheimer's disease- (AD-) associated cognitive deficits globally with these statistics projected to rise over 115.4 million by the year 2050. There is no specific etiology for this cognitive impairment; however, various contributing factors including advancing age (>60 years old), oxidative stress, cerebral injuries, infections, neurologic disorders, and cancer have been implicated. Despite various attempts to manage CI, no curative medicines are yet available. The current drugs used to manage symptoms of AD-associated CI including Donepezil and Rivastigmine among others are only palliative rather than therapeutic. Furthermore, these agents have been associated with undesirable side effects. This calls for alternative and complementary approaches aimed at either preventing or reverting AD-related CI in a curative way without causing adverse events. It is estimated that over 80% of the world's population utilize herbal medicines for basic healthcare as it is considered safe, affordable, and easily accessible as opposed to conventional healthcare. Various parts of P. thonningii are used in traditional medicine to manage various conditions including CI. However, empirical and scientific data to validate these uses is lacking. In this study, the Morris water maze (MWM) experiment was adopted to evaluate the cognitive-enhancing effects of the studied plant extracts. The malondialdehyde (MDA) profiles in the brains of experimental mice were determined using the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) test. Moreover, qualitative phytochemical profiling of the studied plant extracts was performed using standard procedures. The results showed remarkable cognitive-enhancing activities which were reflected in significantly shorter transfer latencies, navigation distances, longer time spent in platform quadrant, and lower MDA levels compared with those recorded for the negative control mice (p < 0.05). Phytochemical screening of the studied plant extracts revealed the presence of antioxidant phytocompounds, which may have played key roles in the extracts' potency. Based on the findings herein, P. thonningii extracts, especially the aqueous ones have a promising potential for the management of AD-associated CI. Further studies aimed at isolating and characterizing specific active compounds for CI from P. thonningii are recommended. Additionally, specific mode(s) of action of active principles should be elucidated. Moreover, toxicity studies should be done on the studied plant extracts to ascertain their safety.
Copyright © 2020 Gervason Apiri Moriasi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest whatsoever regarding this study.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 2018;14(3):367–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.001. - DOI
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Early Signs and Symptoms of Alzheimer’s. Alzheimer’s Association; 2019.
-
- WHO. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017 - 2025.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

