A rapid and accurate method for the detection of four aminoglycoside modifying enzyme drug resistance gene in clinical strains of Escherichia coli by a multiplex polymerase chain reaction
- PMID: 32309051
- PMCID: PMC7153551
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.8944
A rapid and accurate method for the detection of four aminoglycoside modifying enzyme drug resistance gene in clinical strains of Escherichia coli by a multiplex polymerase chain reaction
Abstract
Background: Antibiotics are highly effective drugs used in the treatment of infectious diseases. Aminoglycoside antibiotics are one of the most common antibiotics in the treatment of bacterial infections. However, the development of drug resistance against those medicines is becoming a serious concern.
Aim: This study aimed to develop an efficient, rapid, accurate, and sensitive detection method that is applicable for routine clinical use.
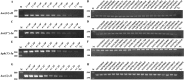
Methods: Escherichia coli was used as a model organism to develop a rapid, accurate, and reliable multiplex polymerase chain reaction (M-PCR) for the detection of four aminoglycoside modifying enzyme (AME) resistance genes Aac(6')-Ib, Aac(3)-II, Ant(3″)-Ia, and Aph(3')-Ia. M-PCR was used to detect the distribution of AME resistance genes in 237 clinical strains of E. coli. The results were verified by simplex polymerase chain reaction (S-PCR).
Results: Results of M-PCR and S-PCR showed that the detection rates of Aac(6')-Ib, Aac(3)-II, Ant(3″)-Ia, and Aph(3')-Ia were 32.7%, 59.2%, 23.5%, and 16.8%, respectively, in 237 clinical strains of E. coli. Compared with the traditional methods for detection and identification, the rapid and accurate M-PCR detection method was established to detect AME drug resistance genes. This technique can be used for the clinical detection as well as the surveillance and monitoring of the spread of those specific antibiotic resistance genes.
Keywords: Aminoglycoside modifying enzyme drug resistance gene; Molecular detection; Multiplex polymerase chain reaction; Polymerase chain reaction.
© 2020 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


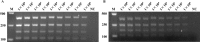
References
-
- Azizi O, Shahcheraghi F, Salimizand H, Modarresi F, Shakibaie MR, Mansouri S, Ramazanzadeh R, Badmasti F, Nikbin V. Molecular analysis and expression of bap gene in biofilm-forming multi-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii. Reports of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2016;5:62–72. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brossier F, Sougakoff W, Aubry A, Bernard C, Cambau E, Jarlier V, Mougari F, Raskine L, Robert J, Veziris N. Molecular detection methods of resistance to antituberculosis drugs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses. 2017;47(5):340–348. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2017.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

