Oxidative stress mediated hepatotoxicity induced by ZNP and modulatory role of fruit extract on male Wistar rat
- PMID: 32309148
- PMCID: PMC7155234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.03.009
Oxidative stress mediated hepatotoxicity induced by ZNP and modulatory role of fruit extract on male Wistar rat
Abstract
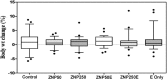
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZNP) are being used in various fields viz cosmetics industry as UV protectants, in the food packaging industry due to their anti-bacterial properties, in agriculture as micronutrients, etc. Increased applications of ZNPs in our day to day life, leading to the contamination of the surrounding environment posing a direct or indirect health risk. Various reports suggest that fruits and vegetables are a rich source of phytochemicals having antioxidant properties which help in neutralizing ROS generated on metal toxicity of the body. The present study focuses to study the ameliorative effect of apple (Pyrus malus) extract (E) on ZNP induced toxicity. Therefore, animals were grouped, six in each, exposed to various doses of ZNP (50 and 250 mg/kg), ZNP (50 and 250 mg/kg)+E. The studied parameters was: food intake, water intake, antioxidants assay, zinc accumulation, and histological alterations and was compared to control. Investigation revealed that ZNP induces toxicity as revealed by the alteration in the studied parameter, whereas those exposed to ZNP along with Pyrus malus fruit extract try to reduce the toxicity induced by nanoparticles but at low doses only. This ameliorative effect of fruit extract might be due to the presence of antioxidants scavenging the free radicals generated by ZNPs suggesting that antioxidant-rich fruit may have a protective role and have the potential to reduce the nanoparticles mediated oxidative stress.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Fruit extract; Nanotoxicity; Oxidative stress; ZNP.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Sharma V., Shukla R.K., Saxena N., Parmar D., Das M., Dhawan A. DNA damaging potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009;185(3):211–218. - PubMed
-
- Prasad T.N.V.K.V., Sudhakar P., Sreenivasulu Y., Latha P., Munaswamy V., Reddy K.R., Sreeprasad T.S., Sajanlal P.R., Pradeep T. Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J. Plant Nutr. 2012;35(6):905–927.
-
- Fan Z., Chang P.C., Lu J.G., Walter E.C., Penner R.M., Lin C.H., Lee H.P. Photoluminescence and polarized photodetection of single ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004;85(25):6128–6130.
-
- Oberdörster G., Maynard A., Donaldson K., Castranova V., Fitzpatrick J., Ausman K., Carter J., Karn B., Kreyling W., Lai D., Olin S. Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: elements of a screening strategy. Part. Fibre Toxicology. 2005;2(1):8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cadenas E. Biochemistry of oxygen toxicity. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1989;58(1):79–110. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

