Dimethyl Fumarate Targets MSK1, RSK1, 2 and IKKα/β Kinases and Regulates NF-κB /p65 Activation in Psoriasis: A Demonstration of the Effect on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, Drawn from Two Patients with Severe Psoriasis Before and After Treatment with Dimethyl Fumarate
- PMID: 32309199
- PMCID: PMC7138529
- DOI: 10.2147/PTT.S234151
Dimethyl Fumarate Targets MSK1, RSK1, 2 and IKKα/β Kinases and Regulates NF-κB /p65 Activation in Psoriasis: A Demonstration of the Effect on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, Drawn from Two Patients with Severe Psoriasis Before and After Treatment with Dimethyl Fumarate
Abstract
Background: Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) has an inhibitory effect on the production of pro-inflammatory proteins from different cells which participate in the immune reaction in psoriatic skin. Most recently it was shown that DMF is an allosteric covalent inhibitor of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinases (RSK1, 2), determined by X-ray crystallography. DMF binds to a specific cysteine residue in RSK2 and in the closely related mitogen and stress-activated kinases 1 (MSK1) which inhibits further downstream activation.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to review the literature on the effects of DMF on activation of MSK1, RSK1, 2 kinases, and downstream transcription factors NF-κB/p65 and IκBα in cells contributing to the pathogenesis of psoriasis. We also hypothesized and studied if treatment with DMF would inhibit the activation of MSK1, RSK1, 2 kinases in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in psoriatic patients.
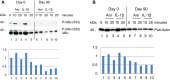
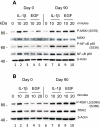
Methods: PBMCs were purified from patients with severe psoriasis before and after 90 days of treatment with DMF. Cells were stimulated with anisomycin, IL-1β or EGF for 10 and 20 minutes. The levels of phosphorylation of MSK1, RSK1, 2 or NF-κB/p65, IκBα were analyzed by Western blotting.
Results: Our case study showed that treatment with DMF inhibited the activation of MSK1 and RSK1, 2 kinases in PBMCs in patients. This supports that DMF is the active metabolite in vivo in psoriatic patients during DMF treatment.
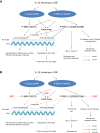
Conclusion: Pro-inflammatory proteins are induced through activation of MSK1 and NF-κB/p65 at (S276). The extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) control cell survival by activating both MSK1 and RSK1, 2 kinases. P-RSK1, 2 activates P-κBα and NF-κB/p65 at (S536). The phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65 at (S276) and (S536) controls different T cell and dendritic cell functions. DMF´s inhibitory effect on MSK1 and RSK1, 2 kinase activations reduces multiple immune reactions in psoriatic patients.
Keywords: 2; DMF; IKKα; IKKβ; IκBα; MSK1; NF-κB/p65; RSK1; psoriasis.
© 2020 Gesser et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Lars Iversen has served as a consultant and/or paid speaker for and/or participated in clinical trials sponsored by: AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Centocor, Eli Lilly, Janssen Cilag, Kyowa, Leo Pharma, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung, UCB. MK Rasmussen has served as a consultant and/or paid speaker for and/or participated in clinical trials sponsored by: AbbVie, Almirall, Eli Lilly, Janssen Cilag, Leo Pharma, Novartis, UCB. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

