Critical physiological and pathological functions of Forkhead Box O tumor suppressors
- PMID: 32309538
- PMCID: PMC6941590
- DOI: 10.15190/d.2013.5
Critical physiological and pathological functions of Forkhead Box O tumor suppressors
Abstract
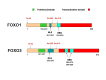
The Forkhead box, subclass O (FOXO) proteins are critical transcription factors, ubiquitously expressed in the human body. These proteins are characterized by a remarkable functional diversity, being involved in cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, oxidative detoxification, DNA damage repair, stem cell maintenance, cell differentiation, cell metabolism, angiogenesis, cardiac development, aging and others. In addition, FOXO have critical implications in both normal and cancer stem cell biology. New strategies to modulate FOXO expression and activity may now be developed since the discovery of novel FOXO regulators and non-coding RNAs (such as microRNAs) targeting FOXO transcription factors. This review focuses on physiological and pathological functions of FOXO proteins and on their action as fine regulators of cell fate and context-dependent cell decisions. A better understanding of the structure and critical functions of FOXO transcription factors and tumor suppressors may contribute to the development of novel therapies for cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: FOX; FOXO; FOXO1; FOXO3; apoptosis; cancer; cancer stem cells; cell cycle; differentiation; metabolism; microRNAs; small non-coding RNAs; stem cells.
Copyright © 2013, Applied Systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
