An Improved Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Analysis of Related Substances of Prednisolone in Active Ingredient
- PMID: 32309709
- PMCID: PMC7161046
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00037
An Improved Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Analysis of Related Substances of Prednisolone in Active Ingredient
Abstract
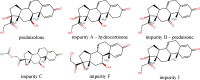
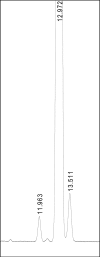
Prednisolone, an important active pharmaceutical ingredient, is a synthetic glucocorticoid used for the preparation of various pharmaceutical products with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It is a challenge in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to separate the prednisolone peak and its structurally related substance (hydrocortisone), which only differs in a double bond at the C-1 position. Successful application of the HPLC method according to the European Pharmacopoeia monograph for related substances of prednisolone is very often limited to the chromatographic system available. This is due to the nonbaseline separation of the prednisolone and hydrocortisone peaks, which is strongly influenced by the instrument parameters and the chosen C18 column. First, an adjusted European Pharmacopoeia method for related substances of prednisolone was developed within the allowable adjustments. Next, an improved stability-indicating reversed-phase HPLC method for related substances of prednisolone was developed and validated for use in quality control laboratories for routine analysis. The optimized separation was performed on a Phenomenex Gemini C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 3 μm) using a gradient mobile-phase system consisting of acetonitrile/tetrahydrofuran/water (15:10:75 v/v/v), acetonitrile/water (80:20 v/v), and ultraviolet detection at 254 nm. A baseline separation was achieved, and stability indicating capability was demonstrated by a forced degradation study. A full validation procedure was performed in accordance with International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use guidelines.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Frew A. J.86 - Glucocorticoids. In Clinical Immunology, Fifth Ed.; Rich R. R.; Fleisher T. A.; Shearer W. T.; Schroeder H. W.; Frew A. J.; Weyand C. M., Eds.; Elsevier: London, 2019; pp 1165–1175.
-
- Papich M. G.Glucocorticoids. In Handbook of Veterinary Pain Management; Third Ed.;, Gaynor J. S.; Muir W. W., Eds.; Mosby: St. Louis, 2015; pp 266–279.
-
- Kim K.-W.; Roh J. K.; Wee H.-J.; Kim C.. Cancer Drug Discovery: Science and History; Springer Netherlands: 2016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

