Blastomycosis in Minnesota, USA, 1999-2018
- PMID: 32310071
- PMCID: PMC7181909
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2605.191074
Blastomycosis in Minnesota, USA, 1999-2018
Abstract
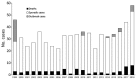
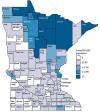
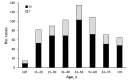
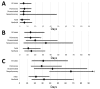
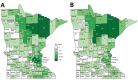
Blastomycosis is a systemic disease caused by Blastomyces spp. fungi. To determine its epidemiology in blastomycosis-endemic Minnesota, USA, we evaluated all cases reported to public health officials during 1999-2018. We focused on time to diagnosis, exposure activities, and exposure location. A total of 671 cases and a median of 34 cases/year were reported. Median time to diagnosis was 31 days; 61% of patients were not tested for blastomycosis until they were hospitalized. The case-fatality rate was 10%, and patients who died were 5.3 times more likely to have a concurrent medical condition. Outdoor activities and soil exposure were reported by many patients, but no specific activity or exposure was common to most. Almost one third of patients were probably exposed in geographic areas other than their home county. Providers should consider alternative etiologies for patients with pneumonia not responding to antibacterial treatment, and public health officials should increase awareness in blastomycosis-endemic areas.
Keywords: Blastomyces; Minnesota; United States; antifungal agents; blastomycosis; delayed diagnosis; endemic diseases; epidemiology; fungi; geography; incidence; inhalation exposure; itraconazole; lung diseases; pneumonia; public health; risk factors; sex ratio; travel; treatment outcome.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

