Description of COVID-19 cases along with the measures taken on prevention and control in Zhejiang, China
- PMID: 32311151
- PMCID: PMC7264658
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25906
Description of COVID-19 cases along with the measures taken on prevention and control in Zhejiang, China
Abstract
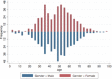
Under the outbreak of COVID-19, it was urgent to analyze the cases from clinical features and epidemiological factors, as well as understand the effectiveness of measures taken on disease prevent and control. A retrospective study was applied for descriptive analysis of clinical features and epidemiological factors of confirmed cases in four cities of Zhejiang. The Onset-admission interval was calculated and plotted as well. The provincial measures regarding the response of COVID-19 were summed up and sorted out. The distribution and sex and age were under normality distribution, and the age of 20 to 80 were all in risk of developing the disease. Clinical features of fever and cough were found mostly happen on patients. More than half of the patients had image changed on chest from reported data. The factor of closely contacted with confirmed cases was the most cause to the disease. The median onset-admission interval was 6 days in Zhejiang province. As of the efficient health system, COVID-19 had been successfully prevented and controlled in Zhejiang. Males and females were all vulnerable to COVID-19. Preventing contact with confirmed cases could largely avoid the disease to happen. The government should take emergent and effective measures to prevent and treatment of the pandemic disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; clinical features; epidemiological factor; provincial measures.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when Novel coronavirus (2019‐nCoV) infection is suspected: interim guidance. https://www.who.int/publications‐detail/clinical‐management‐of‐severe‐ac.... Accessed January on 11, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization . Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) and the virus that causes it. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/technica...
-
- DXY , COVID‐19, Global Pandemic Real‐time Report. 2020. https://ncov.dxy.cn/ncovh5/view/en_pneumonia?from=dxy&source=&link=&share=. Accessed April 6, 2020.
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China . 2020. http://www.nhc.gov.cn. Accessed April 6, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials