COVID-19 and Thrombotic or Thromboembolic Disease: Implications for Prevention, Antithrombotic Therapy, and Follow-Up: JACC State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 32311448
- PMCID: PMC7164881
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.031
COVID-19 and Thrombotic or Thromboembolic Disease: Implications for Prevention, Antithrombotic Therapy, and Follow-Up: JACC State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
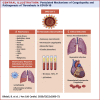
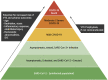
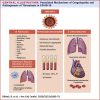
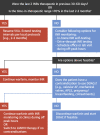
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), a viral respiratory illness caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), may predispose patients to thrombotic disease, both in the venous and arterial circulations, because of excessive inflammation, platelet activation, endothelial dysfunction, and stasis. In addition, many patients receiving antithrombotic therapy for thrombotic disease may develop COVID-19, which can have implications for choice, dosing, and laboratory monitoring of antithrombotic therapy. Moreover, during a time with much focus on COVID-19, it is critical to consider how to optimize the available technology to care for patients without COVID-19 who have thrombotic disease. Herein, the authors review the current understanding of the pathogenesis, epidemiology, management, and outcomes of patients with COVID-19 who develop venous or arterial thrombosis, of those with pre-existing thrombotic disease who develop COVID-19, or those who need prevention or care for their thrombotic disease during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anticoagulant; antiplatelet; antithrombotic therapy; thrombosis.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Rescue fibrinolysis in suspected massive pulmonary embolism during SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.Resuscitation. 2020 Jul;152:86-88. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2020.05.020. Epub 2020 May 20. Resuscitation. 2020. PMID: 32445784 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Spontaneous coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated luminal aortic thrombus.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Aug;160(2):e13-e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.05.024. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32534745 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 and venous thromboembolism: part of a multisystem disease.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 May;113(5):390. doi: 10.17235/reed.2021.7907/2021. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021. PMID: 33733807
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation report - 46. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... Available at: Accessed on March 12 2020.
-
- Clerkin K.J., Fried J.A., Rakhelkar J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2020 Mar 21 [E-pub ahead of print]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

