The effectiveness of intra-articular vs subacromial corticosteroid injection for frozen shoulder: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 32311954
- PMCID: PMC7440081
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019706
The effectiveness of intra-articular vs subacromial corticosteroid injection for frozen shoulder: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Study Protocols.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Nov 7;104(45):e46330. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000046330. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 41204616 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Intra-articular (IA) corticosteroid injection is a commonly used therapy for frozen shoulder (FS), but controversy still exists regarding the injection site with the best outcome. This randomized controlled trial is designed to determine whether corticosteroid injection into the subacromial space was not inferior to IA injection in patients with FS.
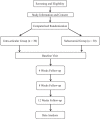
Methods: This study will be a single-center, randomized, and double-blinded trial. Sixty patients who meet inclusion criteria will be randomized in a ratio of 1:1 to either subacromial injection or IA injection group. The outcome evaluations will be conducted at 4 time points (baseline, 4, 8, and 12 weeks after the injection) by an independent physical therapist. The primary outcome measure is visual analog scale for pain, whereas the secondary outcomes include Constant score, and shoulder passive range of motion including abduction, forward elevation, external rotation at the side, and internal rotation at the side.
Discussion: This study has limited inclusion and exclusion criteria and a well-controlled intervention. This clinical trial is expected to provide evidence of proper site of corticosteroid injection for the treatment of FS.
Trial registration: This study protocol was registered in Research Registry (researchregistry5368).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical