An autoinhibitory mechanism controls RNA-binding activity of the nitrate-sensing protein NasR
- PMID: 32314426
- PMCID: PMC7496416
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14517
An autoinhibitory mechanism controls RNA-binding activity of the nitrate-sensing protein NasR
Abstract
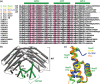
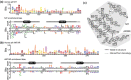
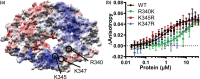
The ANTAR domain harnesses RNA-binding activity to promote transcription attenuation. Although several ANTAR proteins have been analyzed by high-resolution structural analyses, the residues involved in RNA-recognition and transcription attenuation have not been identified. Nor is it clear how signal-responsive domains are allosterically coupled with ANTAR domains for control of gene expression. Herein, we examined the sequence conservation of ANTAR domains to find residues that may associate with RNA. We subjected the corresponding positions of Klebsiella oxytoca NasR to site-directed alanine substitutions and measured RNA-binding activity. This revealed a functionally important patch of residues that forms amino acid pairing interactions with residues from NasR's nitrate-sensing NIT domain. We hypothesize these amino acid pairing interactions are part of an autoinhibitory mechanism that holds the structure in an "off" state in the absence of nitrate signal. Indeed, mutational disruption of these interactions resulted in constitutively active proteins, freed from autoinhibition and no longer influenced by nitrate. Moreover, sequence analyses suggested the autoinhibitory mechanism has been evolutionarily maintained by NasR proteins. These data reveal a molecular mechanism for how NasR couples its nitrate signal to RNA-binding activity, and generally show how signal-responsive domains of one-component regulatory proteins have evolved to exert control over RNA-binding ANTAR domains.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; antiterminator proteins; bacteria; gene expression; nucleic acid; regulatory sequences; transcription attenuation.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

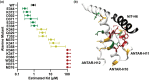

References
-
- Boudes, M. , Lazar, N. , Graille, M. , Durand, D. , Gaidenko, T.A. , Stewart, V. , et al (2012) The structure of the NasR transcription antiterminator reveals a one‐component system with a NIT nitrate receptor coupled to an ANTAR RNA‐binding effector. Molecular Microbiology, 85, 431–444. - PubMed
-
- Bouvet, P. (2009) Identification of nucleic acid high‐affinity binding sequences of proteins by SELEX. Methods in Molecular Biology, 543, 139–150. - PubMed
-
- Chai, W. and Stewart, V. (1998) NasR, a novel RNA‐binding protein, mediates nitrate‐responsive transcription antitermination of the Klebsiella oxytoca M5al nasF operon leader in vitro. Journal of Molecular Biology, 283, 339–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

