Direct Mechanocatalysis: Using Milling Balls as Catalysts
- PMID: 32314837
- PMCID: PMC7589287
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202001177
Direct Mechanocatalysis: Using Milling Balls as Catalysts
Abstract
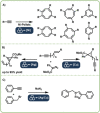
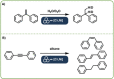
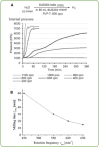
Direct mechanocatalysis describes catalytic reactions under the involvement of mechanical energy with the distinct feature of milling equipment itself being the catalyst. This novel type of catalysis features no solubility challenges of the catalysts nor the substrate and on top offering most facile way of separation.
Keywords: ball milling; cross coupling; heterogeneous catalysis; mechanochemistry; reactive milling.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sheldon R. A., Arends I., Hanefeld U., Green Chemistry and Catalysis, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2007.
-
- Anastas P. T., Warner J. C., Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice, Oxford, 1998.
-
- Rothenberg G., Catalysis: Concepts and Green Applications, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, p. l, 2015.
-
- None
-
- Hernández J. G., Friščić T., Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 4253–4265;
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

