Variability of the Positive Predictive Value of PI-RADS for Prostate MRI across 26 Centers: Experience of the Society of Abdominal Radiology Prostate Cancer Disease-focused Panel
- PMID: 32315265
- PMCID: PMC7373346
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020190646
Variability of the Positive Predictive Value of PI-RADS for Prostate MRI across 26 Centers: Experience of the Society of Abdominal Radiology Prostate Cancer Disease-focused Panel
Abstract
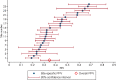
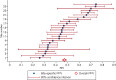
Background Prostate MRI is used widely in clinical care for guiding tissue sampling, active surveillance, and staging. The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) helps provide a standardized probabilistic approach for identifying clinically significant prostate cancer. Despite widespread use, the variability in performance of prostate MRI across practices remains unknown. Purpose To estimate the positive predictive value (PPV) of PI-RADS for the detection of high-grade prostate cancer across imaging centers. Materials and Methods This retrospective cross-sectional study was compliant with the HIPAA. Twenty-six centers with members in the Society of Abdominal Radiology Prostate Cancer Disease-focused Panel submitted data from men with suspected or biopsy-proven untreated prostate cancer. MRI scans were obtained between January 2015 and April 2018. This was followed with targeted biopsy. Only men with at least one MRI lesion assigned a PI-RADS score of 2-5 were included. Outcome was prostate cancer with Gleason score (GS) greater than or equal to 3+4 (International Society of Urological Pathology grade group ≥2). A mixed-model logistic regression with institution and individuals as random effects was used to estimate overall PPVs. The variability of observed PPV of PI-RADS across imaging centers was described by using the median and interquartile range. Results The authors evaluated 3449 men (mean age, 65 years ± 8 [standard deviation]) with 5082 lesions. Biopsy results showed 1698 cancers with GS greater than or equal to 3+4 (International Society of Urological Pathology grade group ≥2) in 2082 men. Across all centers, the estimated PPV was 35% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 27%, 43%) for a PI-RADS score greater than or equal to 3 and 49% (95% CI: 40%, 58%) for a PI-RADS score greater than or equal to 4. The interquartile ranges of PPV at these same PI-RADS score thresholds were 27%-44% and 27%-48%, respectively. Conclusion The positive predictive value of the Prostate Imaging and Reporting Data System was low and varied widely across centers. © RSNA, 2020 Online supplemental material is available for this article. See also the editorial by Milot in this issue.
Figures


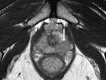
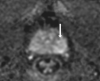
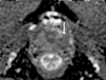
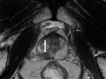
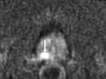
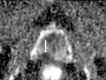
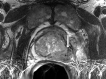
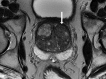
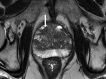
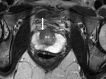
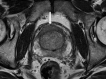
Comment in
-
Variation of PI-RADS Interpretations between Experts: A Significant Limitation.Radiology. 2020 Jul;296(1):85-86. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020192650. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Radiology. 2020. PMID: 32319860 No abstract available.
-
Re: Variability of the Positive Predictive Value of PI-RADS for Prostate MRI Across 26 Centers: Experience of the Society of Abdominal Radiology Prostate Cancer Disease-focused Panel.Eur Urol. 2020 Oct;78(4):633-636. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32859439 No abstract available.
-
Re: Variability of the Positive Predictive Value of PI-RADS for Prostate MRI across 26 Centers: Experience of the Society of Abdominal Radiology Prostate Cancer Disease-Focused Panel.J Urol. 2020 Dec;204(6):1380-1381. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001283. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32960704 No abstract available.
-
Perspectives and Concerns about PI-RADS and Variability.Radiology. 2021 Feb;298(2):E112. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020202340. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 33231533 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Briers E, et al. . EAU–ESTRO–ESUR–SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. https://uroweb.org/guideline/prostate-cancer. Published 2019. Accessed June 24, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Rosenkrantz AB, Hemingway J, Hughes DR, Duszak R, Jr, Allen B, Jr, Weinreb JC. Evolving Use of Prebiopsy Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Medicare Population. J Urol 2018;200(1):89–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

