Laboratory data analysis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) screening in 2510 patients
- PMID: 32315614
- PMCID: PMC7166029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.04.018
Laboratory data analysis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) screening in 2510 patients
Abstract
Background: Novel coronavirus (COVID-19) is highly infectious and requires early detection, isolation, and treatment. We tried to find some useful information by analyzing the covid-19 screening data, so as to provide help for clinical practice.
Method: We collected nucleic acid and hematology data from 2510 patients for COVID-19 infection for retrospective analysis.
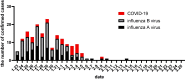
Result: COVID-19 and influenza A and B infection rates were 1.3%, 3%, and 3%, respectively. COVID-19 nucleic acid was detected in stool but not in tear samples from 8 positive patients. Among the 32 patients with COVID-19, 15 (47%) and 16 (50%) patients showed decreased lymphocyte count and lymphocyte ratio, 21(66%) and 24(75%) patients showed decreased eosinophil count and eosinophil ratio, and 18 (56%) patients showed increased C-reactive protein. Ten hematological indicators significantly differed in the blood of patients with COVID-19 and those with influenza A and B (P < 0.05). Eighteen hematological indicators significantly differed between patients with COVID-19 and negative patients (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The positive rate of influenza A and B infection was higher than that of COVID-19. When pharyngeal swab collection may cause infection, fecal samples can be examined. Evaluation of pharyngeal swab and fecal samples can improve the positive rate of nucleic acid detection. The COVID-19 can cause some hematological indices changes.
Keywords: Hematology index; Influenza A; Influenza B; Laboratory data; Novel coronavirus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, WHO Director-General’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020 [EB/ OL], https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at... (accessed 2 February 2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials