A Guide to Targeting the Endocannabinoid System in Drug Design
- PMID: 32316328
- PMCID: PMC7216112
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082778
A Guide to Targeting the Endocannabinoid System in Drug Design
Abstract
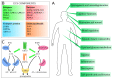
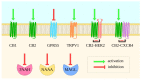
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is one of the most crucial systems in the human organism, exhibiting multi-purpose regulatory character. It is engaged in a vast array of physiological processes, including nociception, mood regulation, cognitive functions, neurogenesis and neuroprotection, appetite, lipid metabolism, as well as cell growth and proliferation. Thus, ECS proteins, including cannabinoid receptors and their endogenous ligands' synthesizing and degrading enzymes, are promising therapeutic targets. Their modulation has been employed in or extensively studied as a treatment of multiple diseases. However, due to a complex nature of ECS and its crosstalk with other biological systems, the development of novel drugs turned out to be a challenging task. In this review, we summarize potential therapeutic applications for ECS-targeting drugs, especially focusing on promising synthetic compounds and preclinical studies. We put emphasis on modulation of specific proteins of ECS in different pathophysiological areas. In addition, we stress possible difficulties and risks and highlight proposed solutions. By presenting this review, we point out information pivotal in the spotlight of ECS-targeting drug design, as well as provide an overview of the current state of knowledge on ECS-related pharmacodynamics and show possible directions for needed research.
Keywords: CB1; CB2; ECS; FAAH; MAGL; endocannabinoid system; molecular target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gaoni Y., Mechoulam R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964;86:1646–1647. doi: 10.1021/ja01062a046. - DOI
-
- Devane W.A., Dysarz F.R., Johnson M.R., Melvin L.S., Howlett A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988;34:605–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

