Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a scoping review
- PMID: 32317050
- PMCID: PMC7175649
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.15.2000125
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a scoping review
Abstract
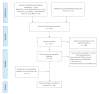
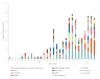
BackgroundIn December 2019, a pneumonia caused by a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) emerged in Wuhan, China and has rapidly spread around the world since then.AimThis study aims to understand the research gaps related to COVID-19 and propose recommendations for future research.MethodsWe undertook a scoping review of COVID-19, comprehensively searching databases and other sources to identify literature on COVID-19 between 1 December 2019 and 6 February 2020. We analysed the sources, publication date, type and topic of the retrieved articles/studies.ResultsWe included 249 articles in this scoping review. More than half (59.0%) were conducted in China. Guidance/guidelines and consensuses statements (n = 56; 22.5%) were the most common. Most (n = 192; 77.1%) articles were published in peer-reviewed journals, 35 (14.1%) on preprint servers and 22 (8.8%) posted online. Ten genetic studies (4.0%) focused on the origin of SARS-CoV-2 while the topics of molecular studies varied. Nine of 22 epidemiological studies focused on estimating the basic reproduction number of COVID-19 infection (R0). Of all identified guidance/guidelines (n = 35), only ten fulfilled the strict principles of evidence-based practice. The number of articles published per day increased rapidly until the end of January.ConclusionThe number of articles on COVID-19 steadily increased before 6 February 2020. However, they lack diversity and are almost non-existent in some study fields, such as clinical research. The findings suggest that evidence for the development of clinical practice guidelines and public health policies will be improved when more results from clinical research becomes available.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; communicable diseases; coronavirus infections; global health emergency; pandemics; scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC PRC). Feb 7: Daily briefing on novel coronavirus cases in China. Beijing: NHC PRC; 7 Feb 2020. Available from: http://en.nhc.gov.cn/2020-02/07/c_76323.htm
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. Geneva: WHO. [Accessed 14 April 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (NHC PRC). Timeline of China's fight against the novel coronavirus. Beijing: NHC PRC; 24 Jan 2020. Available from: http://en.nhc.gov.cn/2020-03/20/c_78021.htm
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Geneva: WHO; 30 Jan 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. Geneva: 11 Mar 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
