Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug Prescription Patterns for Rheumatoid Arthritis Among United States Physicians
- PMID: 32318979
- PMCID: PMC7211222
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-020-00203-w
Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug Prescription Patterns for Rheumatoid Arthritis Among United States Physicians
Abstract
Introduction: Some patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) experience inefficacy or lack of tolerability and hence switch to another TNFi (cycling) or to a therapy with another mode of action (switching). This study examined patient characteristics, prescribing patterns and treatment practice for RA in the United States.
Methods: Data were from the Adelphi Disease Specific Programme (Q2-Q3 2016). Rheumatologists completed a survey and patient record forms for adult patients with RA who had received ≥ 1 targeted therapy. Patients were grouped by class of first-used targeted therapy, and monotherapy vs. combination therapy. TNFi patients who received ≥ 1 targeted therapy were classified as cyclers or switchers. Univariate analyses compared patient characteristics and physician factors across the analysis groups.
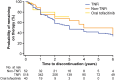
Results: Overall, 631 patients received ≥ 1 targeted therapy; 535 were prescribed a TNFi as first targeted therapy, 53 a nonTNFi biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (bDMARD), and 43 tofacitinib. Of 577 patients with known conventional synthetic (cs) DMARD status, 18.7% were prescribed monotherapy and 81.3% combination therapy. Combination therapy patients received significantly more concomitant medications prior to initiation of first targeted therapy than monotherapy patients (P < 0.05). The top reason for physicians to prescribe first use targeted therapy was strong overall efficacy (79.9%). Of 163 patients who progressed to second targeted therapy, 60.7% were cyclers. A lower proportion of cyclers persisted on their first use targeted therapy versus switchers (P = 0.03). The main reason physicians gave for switching patients at this stage was worsening condition (46.6%).
Conclusions: Most patients were prescribed a TNFi as their first targeted therapy; over half then cycled to another TNFi. This suggests other factors may influence second use targeted treatment choice and highlights the need for greater understanding of outcomes associated with subsequent treatment choices and potential benefits of switching.
Keywords: Biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; Cycling; Rheumatoid arthritis; Switching; Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Emma Sullivan, Jim Kershaw and Stuart Blackburn were employees of Adelphi Real World at the time of this analysis, a company that received funding for the current study from Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Jeannie Choi was an employee of and stockholder in Sanofi at the time of this analysis and is now self-employed. Susan Boklage is an employee of and stockholder in Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Jeffrey Curtis is a consultant to Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Furst DE, Moreland LW, Weisman MH, Birbara CA, et al. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(1):35–45. doi: 10.1002/art.10697. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Keystone EC, Kavanaugh AF, Sharp JT, Tannenbaum H, Hua Y, Teoh LS, et al. Radiographic, clinical, and functional outcomes of treatment with adalimumab (a human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, 52-week trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(5):1400–1411. doi: 10.1002/art.20217. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

