How many chronic myeloid leukemia patients who started a frontline second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor have to switch to a second-line treatment? A retrospective analysis from the monitoring registries of the italian medicines agency (AIFA)
- PMID: 32319737
- PMCID: PMC7300412
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3071
How many chronic myeloid leukemia patients who started a frontline second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor have to switch to a second-line treatment? A retrospective analysis from the monitoring registries of the italian medicines agency (AIFA)
Abstract
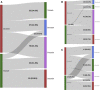
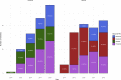
The frequency of patients who switch to a second-line therapy from a frontline second-generation (2gen) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) such as dasatinib and nilotinib, is still substantially unknown. We retrospectively investigated a large series of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CP-CML) patients initially treated with 2gen TKIs monitored through the Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA Agenzia Italiana del farmaco) registries. Overall, 2420 patients were analyzed over a period of 6 years. One hundred and fifty-seven patients (16.3%) treated with dasatinib and 164 treated with nilotinib (11.3%) have switched to another drug, with an overall frequency of 13.2%. In the dasatinib cohort, 39.4% of patients changed treatment for failure and 36.3% for intolerance as compared to 45.7% and 27.4% respectively in the nilotinib cohort. Overall, the median time to switch due to resistance was 293 days, whereas it was 317 days in case of intolerance. Resistance was observed mainly in younger male patients with high-risk features, while intolerance was not related to any baseline parameter. After resistance/intolerance to nilotinib, the majority of patients switched to dasatinib (53.8%) whereas in case of frontline dasatinib to ponatinib (43.2%). To the best of our knowledge these data provide the first report on the frequency of discontinuation of frontline 2gen TKIs and on the main causes and pattern of choice to a second-line therapy in the real-life setting.
Keywords: chronic myeloid leukemia; failure; intolerance; second-generation TKIs.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MB received honoraria by Novartis, Incyte, Pfizer, Celgene; all the other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS, et al. Imatinb for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: incidence of sustained responses in an intention‐to‐treat analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3358‐3363. - PubMed
-
- Hochhaus A, O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, et al. Six‐year follow‐up of patients receiving imatinib for the first‐line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2009;23:1054‐1061. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

