Recent Insights Into the Regulation of Coagulation and Thrombosis
- PMID: 32320291
- PMCID: PMC7182067
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.312674
Recent Insights Into the Regulation of Coagulation and Thrombosis
Abstract
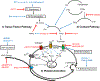
Hemostatic clot formation is the result of a balance between the procoagulant system responding to tissue trauma and the anticoagulant system, which restricts clot formation to the injury site. Imbalances in coagulation lead to a tendency towards either thrombosis or bleeding. Over the past two years, studies published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology have provided insights into the regulation of this crucial system. Here, we highlight recent discoveries concerning the two pathways of thrombin formation, the extrinsic tissue factor (TF) pathway and the intrinsic contact pathway, and the contributions of platelet activation to the thrombotic process.
Keywords: anticoagulants; factor VIIa; glycoproteins; platelet activation; thrombin.
Figures
References
-
- Komiyama Y, Pedersen AH, Kisiel W. Proteolytic activation of human factors ix and x by recombinant human factor viia: Effects of calcium, phospholipids, and tissue factor. Biochemistry. 1990;29:9418–9425. - PubMed
-
- Del Conde I, Shrimpton CN, Thiagarajan P, Lopez JA. Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood. 2005;106:1604–1611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

