Impact of population movement on the spread of 2019-nCoV in China
- PMID: 32321369
- PMCID: PMC7269026
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1760143
Impact of population movement on the spread of 2019-nCoV in China
Abstract
Since Dec 2019, China has experienced an outbreak caused by a novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV. A travel ban was implemented for Wuhan, Hubei on Jan 23 to slow down the outbreak. We found a significant positive correlation between population influx from Wuhan and confirmed cases in other cities across China (R2 = 0.85, P < 0.001), especially cities in Hubei (R2 = 0.88, P < 0.001). Removing the travel restriction would have increased 118% (91%-172%) of the overall cases for the coming week, and a travel ban taken three days or a week earlier would have reduced 47% (26%-58%) and 83% (78%-89%) of the early cases. We would expect a 61% (48%-92%) increase of overall cumulative cases without any restrictions on returning residents, and 11% (8%-16%) increase if the travel ban stays in place for Hubei. Cities from Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and Capital Economic Circle regions are at higher risk.
Keywords: 2019-nCov; population movement; risk; spread; travel ban.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
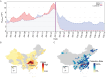
References
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Update on novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) up to 12 p.m. of Feb 14. Feb 15, 2020. [cited 2020 Feb 24]. Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202002/50994e4df10c49c199ce6db07e196b61.s... (in Chinese).
-
- WHO. Novel coronavirus—China. Jan 12, 2020. [cited 2020 Feb 24]. Available from: https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/.
-
- Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team. [The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(2):145–151.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
