Fly eyes are not still: a motion illusion in Drosophila flight supports parallel visual processing
- PMID: 32321749
- PMCID: PMC7272343
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.212316
Fly eyes are not still: a motion illusion in Drosophila flight supports parallel visual processing
Abstract
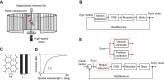
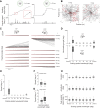
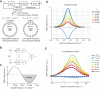
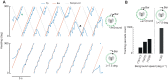
Most animals shift gaze by a 'fixate and saccade' strategy, where the fixation phase stabilizes background motion. A logical prerequisite for robust detection and tracking of moving foreground objects, therefore, is to suppress the perception of background motion. In a virtual reality magnetic tether system enabling free yaw movement, Drosophila implemented a fixate and saccade strategy in the presence of a static panorama. When the spatial wavelength of a vertical grating was below the Nyquist wavelength of the compound eyes, flies drifted continuously and gaze could not be maintained at a single location. Because the drift occurs from a motionless stimulus - thus any perceived motion stimuli are generated by the fly itself - it is illusory, driven by perceptual aliasing. Notably, the drift speed was significantly faster than under a uniform panorama, suggesting perceptual enhancement as a result of aliasing. Under the same visual conditions in a rigid-tether paradigm, wing steering responses to the unresolvable static panorama were not distinguishable from those to a resolvable static pattern, suggesting visual aliasing is induced by ego motion. We hypothesized that obstructing the control of gaze fixation also disrupts detection and tracking of objects. Using the illusory motion stimulus, we show that magnetically tethered Drosophila track objects robustly in flight even when gaze is not fixated as flies continuously drift. Taken together, our study provides further support for parallel visual motion processing and reveals the critical influence of body motion on visuomotor processing. Motion illusions can reveal important shared principles of information processing across taxa.
Keywords: Control; Feedback; Motion vision; Saccade; Stability.
© 2020. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aptekar J. W., Keles M. F., Mongeau J.-M., Lu P. M., Frye M. A. and Shoemaker P. A. (2014). Method and software for using m-sequences to characterize parallel components of higher-order visual tracking behavior in Drosophila. Front. Neural Circuits 8, 130 10.3389/fncir.2014.00130 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

