The receptor tyrosine kinase EPHB6 regulates catecholamine exocytosis in adrenal gland chromaffin cells
- PMID: 32321761
- PMCID: PMC7261780
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013251
The receptor tyrosine kinase EPHB6 regulates catecholamine exocytosis in adrenal gland chromaffin cells
Abstract
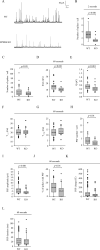
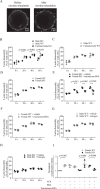
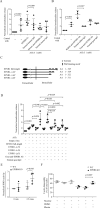
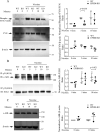
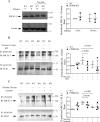
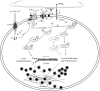
The erythropoietin-producing human hepatocellular receptor EPH receptor B6 (EPHB6) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that has been shown previously to control catecholamine synthesis in the adrenal gland chromaffin cells (AGCCs) in a testosterone-dependent fashion. EPHB6 also has a role in regulating blood pressure, but several facets of this regulation remain unclear. Using amperometry recordings, we now found that catecholamine secretion by AGCCs is compromised in the absence of EPHB6. AGCCs from male knockout (KO) mice displayed reduced cortical F-actin disassembly, accompanied by decreased catecholamine secretion through exocytosis. This phenotype was not observed in AGCCs from female KO mice, suggesting that testosterone, but not estrogen, contributes to this phenotype. Of note, reverse signaling from EPHB6 to ephrin B1 (EFNB1) and a 7-amino acid-long segment in the EFNB1 intracellular tail were essential for the regulation of catecholamine secretion. Further downstream, the Ras homolog family member A (RHOA) and FYN proto-oncogene Src family tyrosine kinase (FYN)-proto-oncogene c-ABL-microtubule-associated monooxygenase calponin and LIM domain containing 1 (MICAL-1) pathways mediated the signaling from EFNB1 to the defective F-actin disassembly. We discuss the implications of EPHB6's effect on catecholamine exocytosis and secretion for blood pressure regulation.
Keywords: EPHB6; F-actin; actin; adrenal; adrenal gland chromaffin cell; catecholamine; exocytosis; receptor tyrosine kinase.
© 2020 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

