Maize Plant Architecture Is Regulated by the Ethylene Biosynthetic Gene ZmACS7
- PMID: 32321843
- PMCID: PMC7333711
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.19.01421
Maize Plant Architecture Is Regulated by the Ethylene Biosynthetic Gene ZmACS7
Abstract
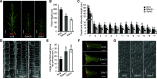
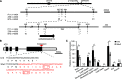
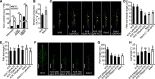
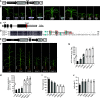
Plant height and leaf angle are two crucial determinants of plant architecture in maize (Zea mays) and are closely related to lodging resistance and canopy photosynthesis at high planting density. These two traits are primarily regulated by several phytohormones. However, the mechanism of ethylene in regulating plant architecture in maize, especially plant height and leaf angle, is unclear. Here, we characterized a maize mutant, Semidwarf3 (Sdw3), which exhibits shorter stature and larger leaf angle than the wild type. Histological analysis showed that inhibition of longitudinal cell elongation in the internode and promotion in the auricle were mainly responsible for reduced plant height and enlarged leaf angle in the Sdw3 mutant. Through positional cloning, we identified a transposon insertion in the candidate gene ZmACS7, encoding 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) Synthase 7 in ethylene biosynthesis of maize. The transposon alters the C terminus of ZmACS7. Transgenic analysis confirmed that the mutant ZmACS7 gene confers the phenotypes of the Sdw3 mutant. Enzyme activity and protein degradation assays indicated that the altered C terminus of ZmACS7 in the Sdw3 mutant increases this protein's stability but does not affect its catalytic activity. The ACC and ethylene contents are dramatically elevated in the Sdw3 mutant, leading to reduced plant height and increased leaf angle. In addition, we demonstrated that ZmACS7 plays crucial roles in root development, flowering time, and leaf number, indicating that ZmACS7 is an important gene with pleiotropic effects during maize growth and development.
© 2020 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phenotypic characterization and genetic mapping of the semi-dwarf mutant sdw9 in maize.Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Oct 21;137(11):253. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04762-2. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 39433551
-
Maize plant architecture trait QTL mapping and candidate gene identification based on multiple environments and double populations.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Mar 11;22(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03470-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35277127 Free PMC article.
-
Leaf angle regulation toward a maize smart canopy.Plant J. 2025 Jan;121(2):e17208. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17208. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 39661752 Review.
-
Tissue-specific expression of the ethylene biosynthetic machinery regulates root growth in maize.Plant Mol Biol. 2009 Jan;69(1-2):195-211. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9418-1. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18979169
-
Exploiting SPL genes to improve maize plant architecture tailored for high-density planting.J Exp Bot. 2018 Sep 14;69(20):4675-4688. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery258. J Exp Bot. 2018. PMID: 29992284 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of flag leaf morphology identifies a major genomic region controlling flag leaf angle in the US winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Aug 14;137(9):205. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04701-1. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 39141073 Free PMC article.
-
Study on ZmRPN10 Regulating Leaf Angle in Maize by RNA-Seq.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 22;24(1):189. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010189. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613631 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of quantitative trait loci for lodging and related agronomic traits in soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.).BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 30;25(1):900. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10794-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39350068 Free PMC article.
-
Fine mapping of candidate quantitative trait loci for plant and ear height in a maize nested-association mapping population.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 4;13:963985. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.963985. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35991429 Free PMC article.
-
Joint-GWAS, Linkage Mapping, and Transcriptome Analysis to Reveal the Genetic Basis of Plant Architecture-Related Traits in Maize.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 26;25(5):2694. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052694. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken RM, Smucker AJ(1996) Root system regulation of whole plant growth. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34: 325–346 - PubMed
-
- Argueso CT, Hansen M, Kieber JJ(2007) Regulation of ethylene biosynthesis. J Plant Growth Regul 26: 92–105
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

