Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, Flk1 and Flt1, in rat skin mast cells during development
- PMID: 32321901
- PMCID: PMC7324820
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.20-0092
Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors, Flk1 and Flt1, in rat skin mast cells during development
Abstract
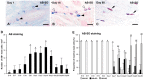
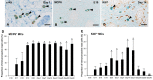
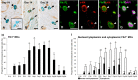
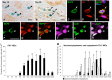
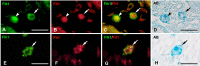
Vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) is a principal regulator of hematopoiesis as well as angiogenesis. However, the functions of VEGF-A and its receptors (VEGFRs) in the differentiation of mast cells (MCs) in the skin remain unclear. The aim of this study was to determine the expression patterns of two VEGFRs (Flk1 and Flt1) in the skin MCs during development and maturation in rats. From the 17th days of embryonic development (E17) to 1 day after birth (Day 1), most of skin MCs were immature cells containing predominant alcian blue (AB)+ rather than safranin O (SO)+ granules (AB>SO MCs). AB>SO MC proportions gradually decreased, while mature AB<SO MC proportions increased from Day 7 to 28. Flk1+ MC proportions increased from E20 and reached to approximately 90% from Day 1 to 21, thereafter decreased to about 10% at Day 60 and 90. Flk1+ MC proportions changed almost in parallel with the numbers of MCs and Ki67+ MC proportions from E17 to Day 90. The proportions of MCs with both nuclear and cytoplasmic Flt1-immunoreactivity were markedly increased at Day 28, when the proportions of nuclear Flk1+, Ki67+, and AB>SO MCs had significantly decreased, and AB<SO MC proportions significantly increased. Considering that the main function of Flt1 is suppression of Flk1 effects, our results indicated that cross-talk between Flk1 and Flt1 regulates the proliferation and maturation of the skin MCs during late embryonic and neonatal development in rats.
Keywords: Flk1; Flt1; mast cell; rat; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alterations in the immunohistochemical distribution patterns of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors Flk1 and Flt1 in bleomycin-induced rat lung fibrosis.Virchows Arch. 1999 Jul;435(1):20-31. doi: 10.1007/s004280050390. Virchows Arch. 1999. PMID: 10431842
-
Distinct expression patterns of Flk1 and Flt1 in the coronary vascular system during development and after myocardial infarction.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 1;495(1):884-891. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.094. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29158084
-
Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors Flt1 and Flk1.Nat Med. 2003 Jul;9(7):936-43. doi: 10.1038/nm884. Nat Med. 2003. PMID: 12796773
-
The role of VEGF and VEGFR2/Flk1 in proliferation of retinal progenitor cells in murine retinal degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Sep;48(9):4315-20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0354. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17724222
-
On Connective Tissue Mast Cells as Protectors of Life, Reproduction, and Progeny.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 19;25(8):4499. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084499. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674083 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mast Cells in the Skin: Defenders of Integrity or Offenders in Inflammation?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 27;22(9):4589. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094589. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast Cell Activation Syndrome Update-A Dermatological Perspective.J Pers Med. 2023 Jul 10;13(7):1116. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071116. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37511729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed A., Dunk C., Kniss D., Wilkes M.1997. Role of VEGF receptor-1 (Flt-1) in mediating calcium-dependent nitric oxide release and limiting DNA synthesis in human trophoblast cells. Lab. Invest. 76: 779–791. - PubMed
-
- Bahramsoltani M., De Spiegelaere W., Janczyk P., Hiebl B., Cornillie P., Plendl J.2010. Quantitation of angiogenesis in vitro induced by VEGF-A and FGF-2 in two different human endothelial cultures-an all-in-one assay. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 46: 189–202. doi: 10.3233/CH-2010-1345 - DOI - PubMed

