Orthosteric muscarinic receptor activation by the insect repellent IR3535 opens new prospects in insecticide-based vector control
- PMID: 32321987
- PMCID: PMC7176678
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-63957-x
Orthosteric muscarinic receptor activation by the insect repellent IR3535 opens new prospects in insecticide-based vector control
Abstract
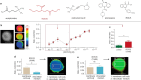
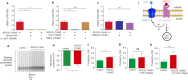
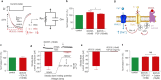
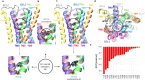
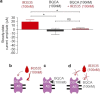
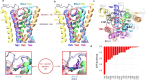
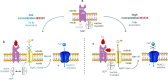
The insect repellent IR3535 is one of the important alternative in the fight against mosquito-borne disease such as malaria, dengue, chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika. Using a multidisciplinary approach, we propose the development of an innovative insecticide-based vector control strategy using an unexplored property of IR3535. We have demonstrated that in insect neurosecretory cells, very low concentration of IR3535 induces intracellular calcium rise through cellular mechanisms involving orthosteric/allosteric sites of the M1-muscarinic receptor subtype, G protein βγ subunits, background potassium channel inhibition generating depolarization, which induces voltage-gated calcium channel activation. The resulting internal calcium concentration elevation increases nicotinic receptor sensitivity to the neonicotinoid insecticide thiacloprid. The synergistic interaction between IR3535 and thiacloprid contributes to significantly increase the efficacy of the treatment while reducing concentrations. In this context, IR3535, used as a synergistic agent, seems to promise a new approach in the optimization of the integrated vector management for vector control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

