Potential Implications of Interactions between Fe and S on Cereal Fe Biofortification
- PMID: 32325653
- PMCID: PMC7216021
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082827
Potential Implications of Interactions between Fe and S on Cereal Fe Biofortification
Abstract
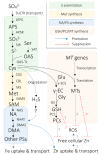
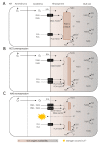
Iron (Fe) and sulfur (S) are two essential elements for plants, whose interrelation is indispensable for numerous physiological processes. In particular, Fe homeostasis in cereal species is profoundly connected to S nutrition because phytosiderophores, which are the metal chelators required for Fe uptake and translocation in cereals, are derived from a S-containing amino acid, methionine. To date, various biotechnological cereal Fe biofortification strategies involving modulation of genes underlying Fe homeostasis have been reported. Meanwhile, the resultant Fe-biofortified crops have been minimally characterized from the perspective of interaction between Fe and S, in spite of the significance of the crosstalk between the two elements in cereals. Here, we intend to highlight the relevance of Fe and S interrelation in cereal Fe homeostasis and illustrate the potential implications it has to offer for future cereal Fe biofortification studies.
Keywords: Fe and S interaction; Fe biofortification; Strategy I; Strategy II; cereals; nicotianamine; phytosiderophores.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . The Global Prevalence of Anemia in 2011. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015.
-
- Graham R.D., Welch R.M., Bouis H.E. Addressing micronutrient malnutrition through enhancing the nutritional quality of staple foods: Principles, perspectives and knowledge gaps. Adv. Agron. 2001;70:77–142.
-
- Bouis H.E., Welch R.M. Biofortification—A sustainable agricultural strategy for reducing micronutrient malnutrition in the Global South. Crop Sci. 2010;50(Suppl. 1):S20–S32. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2009.09.0531. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

