Personalized Medicine: Recent Progress in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 32325878
- PMCID: PMC7226371
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12041009
Personalized Medicine: Recent Progress in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
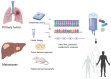
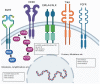
Translational research has revolutionized how we develop new treatments for cancer patients. The change from an organ-centric concept guiding treatment choice towards deep molecular analysis, driving a personalized approach, is one of the most important advances of modern oncology. Several tools such as next generation sequencing and RNA sequencing have greatly improved the capacity to detect predictive and prognostic molecular alterations. Detection of gene mutations, amplifications, and fusions has therefore altered the history of several diseases in both a localized and metastatic setting. This shift in perspective, in which attention is focused on the specific molecular alterations of the tumor, has opened the door to personalized treatment. This situation is reflected in the increasing number of basket trials selecting specific molecular targets. Nonetheless, some weaknesses need to be addressed. The complexity of cancer cells enriched with concomitant molecular alterations complicates identification of the driver. Moreover, tumor heterogeneity could be responsible for the lack of benefit when targeted agents are used. In light of this, there is growing interest in the role of multidisciplinary committees or molecular tumor boards to try to enhance selection. The aim of this review is to critically analyze the evolution of cancer treatment towards a precision approach, underlining some recent successes and unexpected failures.
Keywords: new drug development; personalized medicine; precision medicine; translational oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C. declares institutional research funding from Genentech, Merck Serono, BMS, MSD, Roche, Beigene, Bayer, Servier, Lilly, Novartis, Takeda, Astellas and Fibrogen and advisory board or speaker fees from Merck Serono, Roche, Servier, Takeda and Astellas in the last 5 years. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

