Structural basis of ER-associated protein degradation mediated by the Hrd1 ubiquitin ligase complex
- PMID: 32327568
- PMCID: PMC7380553
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaz2449
Structural basis of ER-associated protein degradation mediated by the Hrd1 ubiquitin ligase complex
Abstract
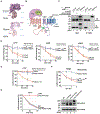
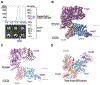
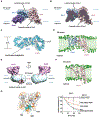
Misfolded luminal endoplasmic reticulum (ER) proteins undergo ER-associated degradation (ERAD-L): They are retrotranslocated into the cytosol, polyubiquitinated, and degraded by the proteasome. ERAD-L is mediated by the Hrd1 complex (composed of Hrd1, Hrd3, Der1, Usa1, and Yos9), but the mechanism of retrotranslocation remains mysterious. Here, we report a structure of the active Hrd1 complex, as determined by cryo-electron microscopy analysis of two subcomplexes. Hrd3 and Yos9 jointly create a luminal binding site that recognizes glycosylated substrates. Hrd1 and the rhomboid-like Der1 protein form two "half-channels" with cytosolic and luminal cavities, respectively, and lateral gates facing one another in a thinned membrane region. These structures, along with crosslinking and molecular dynamics simulation results, suggest how a polypeptide loop of an ERAD-L substrate moves through the ER membrane.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
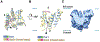
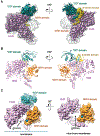
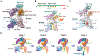
Comment in
-
ER-associated Protein Degradation at Atomic Resolution.Trends Biochem Sci. 2020 Sep;45(9):723-725. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.06.005. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020. PMID: 32616332
-
Taking out the trash: How misfolded proteins are removed from the endoplasmic reticulum.Fac Rev. 2022 Oct 5;11:29. doi: 10.12703/r-01-0000018. eCollection 2022. Fac Rev. 2022. PMID: 36267301 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

