Translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments
- PMID: 32327746
- PMCID: PMC7178926
- DOI: 10.1038/s41584-020-0419-z
Translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments
Abstract
In 1973, IL-6 was identified as a soluble factor that is secreted by T cells and is important for antibody production by B cells. Since its discovery more than 40 years ago, the IL-6 pathway has emerged as a pivotal pathway involved in immune regulation in health and dysregulation in many diseases. Targeting of the IL-6 pathway has led to innovative therapeutic approaches for various rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, adult-onset Still's disease, giant cell arteritis and Takayasu arteritis, as well as other conditions such as Castleman disease and cytokine release syndrome. Targeting this pathway has also identified avenues for potential expansion into several other indications, such as uveitis, neuromyelitis optica and, most recently, COVID-19 pneumonia. To mark the tenth anniversary of anti-IL-6 receptor therapy worldwide, we discuss the history of research into IL-6 biology and the development of therapies that target IL-6 signalling, including the successes and challenges and with an emphasis on rheumatic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
E.H.C. has received research grants from Bio-Cancer, Biogen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB; consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Chugai Pharma, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, R-Pharm and Sanofi; speaker’s fees from Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharma, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi and UCB. F.D.B. has received research grants from AbbVie, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Novimmune and SOBI. T.T. has received research grants from AbbVie, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Astellas Pharma, AYUMI Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis Pharma K.K., Pfizer Japan, Takeda Pharmaceutical; and personal fees from AbbVie G.K., Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca K.K., Bristol-Myers K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis Pharma K.K., Pfizer Japan, Sanofi K.K., Teijin Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Taisho Pharmaceutical, Takeda Pharmaceutical, UCB Japan. M.H. is an employee of Chugai Pharmaceutical. M.R.J. is employed by Roche and owns shares in Roche. T.K. has a patent for tocilizumab. Work by T.K.’s group is supported in part by the Kishimoto Foundation.
Figures
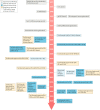

References
-
- Kishimoto T, Ishizaka K. Regulation of antibody response in vitro. VII. Enhancing soluble factors for IgG and IgE antibody response. J. Immunol. 1973;111:1194–1205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

