SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes
- PMID: 32327758
- PMCID: PMC8637938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6
SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes
Abstract
We investigated SARS-CoV-2 potential tropism by surveying expression of viral entry-associated genes in single-cell RNA-sequencing data from multiple tissues from healthy human donors. We co-detected these transcripts in specific respiratory, corneal and intestinal epithelial cells, potentially explaining the high efficiency of SARS-CoV-2 transmission. These genes are co-expressed in nasal epithelial cells with genes involved in innate immunity, highlighting the cells' potential role in initial viral infection, spread and clearance. The study offers a useful resource for further lines of inquiry with valuable clinical samples from COVID-19 patients and we provide our data in a comprehensive, open and user-friendly fashion at www.covid19cellatlas.org.
Figures
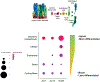
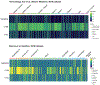
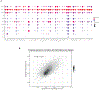


Update of
-
SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes Are Most Highly Expressed in Nasal Goblet and Ciliated Cells within Human Airways.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2020 Mar 13:arXiv:2003.06122v1. ArXiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Med. 2020 May;26(5):681-687. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6. PMID: 32550242 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Options for Personal Protective Equipment During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Used in New Orleans, Louisiana.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020 Sep;8(8):2481-2483. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.05.021. Epub 2020 May 30. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020. PMID: 32485236 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical characteristics associated with persistent olfactory and taste alterations in COVID-19: A preliminary report on 121 patients.Am J Otolaryngol. 2020 Sep-Oct;41(5):102548. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102548. Epub 2020 May 26. Am J Otolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32516656 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. (2020). Retrieved from https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica...
Methods-only References
-
- Kucharski AJ & Althaus CL Euro surveillance : bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles 20, 14–18 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, et al. Nature medicine (2020).
-
- Guan WJ, et al. N Engl J Med (2020).
Grants and funding
- MR/S036334/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K08 HL130595/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NC/N001540/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- MR/S005579/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL148856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PB-PG-1215-20037/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- K08 HL146943/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S035826/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S035907/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- NC/T2T0419/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- G0900879/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/16/47/32156/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL146557/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL135124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL145567/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0701448/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17230/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P009581/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/19/1/34461/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL127349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145372/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K017047/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R24 HD000836/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI118672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_12009/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R015635/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R006237/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

