Stabilization of betalains by encapsulation-a review
- PMID: 32327769
- PMCID: PMC7171008
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-019-04120-x
Stabilization of betalains by encapsulation-a review
Abstract
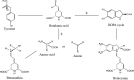
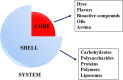
Betalains are pigments that have properties that benefit health, such as antioxidant, anticancer, and antimicrobial activity, and they also possess a high ability to provide color. However, these pigments, although used as colorants in certain foods, have not been able to be potentialized to diverse areas such as pharmacology, due to their instability to physicochemical factors such as high temperature, pH changes and high water activity. For this reason, different stabilization methods have been reported. The method that has presented best results for diversifying the use of betalains has been encapsulation. Encapsulation is a method of entrapment where the objective is to protect a compound utilizing more stable matrices from encapsulation technologies. This method has been employed to provide greater stability to betalains, using different matrices and encapsulation technologies. However, a review does not exist, to our knowledge, which analyzes the effect of matrices and encapsulation technologies on betalains stabilization. Therefore, the objective of this review article was to evaluate the different matrices and encapsulation techniques that have been employed to stabilize betalains, in order to arrive at specific conclusions concerning the effect of encapsulation on their stabilization and to propose new techniques and matrices that could promote their stabilization.
Keywords: Betalains; Effects; Encapsulation; Matrix; Stabilization.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2019.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar TS, Mamani NW, Espinoza SC, Basilio AJ, Condezo HL. Microencapsulated betacyanin from colored organic quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd): optimization, physicochemical characterization and accelerated storage stability. J Sci of Food Agric. 2018;98:5873–5883. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar MJ, Jacquot M, Jasniewski J, Jacquot C, Imran M, Jamshidian Desobry S. Antioxidant capacity and light-aging study of HPMC films functionalized with natural plant extract. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;89:1150–1158. - PubMed
-
- Amjadi S, Ghorbani M, Hamishehkar H, Roufegarinejad L. Improvement in the stability of betanin by liposomal nanocarriers: its application in gummy candy as a food model. Food Chem. 2018;256:156–162. - PubMed
-
- Amjadi S, Abbasi MM, Shokouhi B, Ghorbani M, Hamishehkar H. Enhancement of therapeutic efficacy of betanin for diabetes treatment by liposomal nanocarriers. J Funct Foods. 2019;59:119–128.
-
- Atigo JLD, Bergamasco RDC, Madrona GS. Effect of ph on the stability of red beet extract (Beta vulgaris l) microcapsules produced by spray drying or freeze drying. Food Sci Technol. 2018;38:72–77.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources