Establishment of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI)
- PMID: 32327886
- PMCID: PMC7164986
- DOI: 10.2337/cd19-0032
Establishment of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI)
Erratum in
-
Erratum. Establishment of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative (T1DX-QI). Clinical Diabetes 2020;38:141-151 (DOI: 10.2337/cd19-0032).Clin Diabetes. 2020 Jul;38(3):322. doi: 10.2337/cd20-er03. Clin Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32694883 Free PMC article.
Abstract
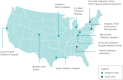
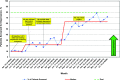
The T1D Exchange established a learning platform by evaluating the current state of care and engaging 10 diabetes clinics in collaborative quality improvement (QI) activities. Participating clinics are sharing data and best practices to improve care delivery for people with type 1 diabetes. This article describes the design and initial implementation of this platform, known as the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative. This effort has laid a foundation for learning from variation in type 1 diabetes care delivery via QI methodology and has demonstrated success in improving processes through iterative testing cycles and transparent sharing of data.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National diabetes statistics report. Available from www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics/statistics-report.html. Accessed 24 August 2018
-
- DiMeglio LA, Acerini CL, Codner E, et al. . ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: glycemic control targets and glucose monitoring for children, adolescents, and young adults with diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19(Suppl. 27):105–114 - PubMed
-
- Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, et al. .; T1D Exchange Clinic Network . Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care 2015;38:971–978 - PubMed

