Comparison of Figulla Flex® and Amplatzer™ devices for atrial septal defect closure: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 32329042
- PMCID: PMC8078976
- DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0058
Comparison of Figulla Flex® and Amplatzer™ devices for atrial septal defect closure: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Atrial septal defect (ASD) is one of the most common congenital heart diseases. Percutaneous closure is the preferred treatment, but certain complications remain a concern. The most common devices are AMPLATZER™ (ASO) (St. Jude Medical, St. Paul, MN, USA) and Figulla Flex® septal occluders (FSO) (Occlutech GmbH, Jena, Germany). The present study aimed to assess main differences in outcomes.
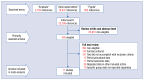
Methods: A systematic search in Pubmed and Google scholarship was performed by two independent reviewers for any study comparing ASO and FSO. Searched terms were "Figulla", "Amplatzer", and "atrial septal defect". A random-effects model was used.
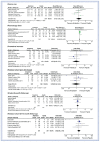
Results: A total of 11 studies including 1770 patients (897 ASO; 873 FSO) were gathered. Baseline clinical and echocardiographic characteristics were comparable although septal aneurysm was more often reported in patients treated with ASO (32% vs. 25%; p = 0.061). Success rate (94% vs. 95%; OR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.38-1.71; p = 0.58) and peri-procedural complications were comparable. Procedures were shorter, requiring less fluoroscopy time with an FSO device (OR: 0.59; 95% CI: 0.20-0.97; p = 0.003). Although the global rate of complications in long-term was similar, the ASO device was associated with a higher rate of supraventricular arrhythmias (14.7% vs. 7.8%, p = 0.009).
Conclusions: Percutaneous closure of ASD is a safe and effective, irrespective of the type of device. No differences exist regarding procedural success between the ASO and FSO devices but the last was associated to shorter procedure time, less radiation, and lower rate of supraventricular arrhythmias in follow-up. Late cardiac perforation did not occur and death in the follow-up was exceptional.
Keywords: Amplatzer; Figulla; atrial septal defect.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect with the Figulla(®) ASD Occluder: a comparative study with the Amplatzer(®) Septal Occluder.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Jan;108(1):57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25453168
-
Figulla ASD occluder versus Amplatzer Septal Occluder: a comparative study on validation of a novel device for percutaneous closure of atrial septal defects.J Interv Cardiol. 2009 Dec;22(6):489-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8183.2009.00497.x. Epub 2009 Sep 3. J Interv Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19735475
-
Efficacy and safety of atrial septal defect closure using Occlutech Figulla Flex II compared with Amplatzer Septal Occluder.Heart Vessels. 2021 May;36(5):704-709. doi: 10.1007/s00380-020-01739-1. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Heart Vessels. 2021. PMID: 33386412
-
Safety and Efficacy of the Amplatzer Septal Occluder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2022 Apr;37:52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2021.06.002. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2022. PMID: 34183276 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with percutaneous atrial septal closure device: Electrophysiology Collaborative Consortium for Meta-analysis-ELECTRAM Investigators.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020 Sep;31(9):2328-2334. doi: 10.1111/jce.14616. Epub 2020 Jun 25. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020. PMID: 32530528
References
-
- Ilkay E, Kaçmaz F, Ozeke O, et al. The efficiency and safety of percutaneous closure of secundum atrial septal defects with the Occlutech Figulla device: initial clinical experience. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2010;38(3):189–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

