Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19
- PMID: 32329756
- PMCID: PMC7308057
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.138999
Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19
Abstract
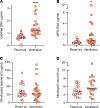
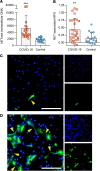
In severe cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), viral pneumonia progresses to respiratory failure. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are extracellular webs of chromatin, microbicidal proteins, and oxidant enzymes that are released by neutrophils to contain infections. However, when not properly regulated, NETs have the potential to propagate inflammation and microvascular thrombosis - including in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. We now report that sera from patients with COVID-19 have elevated levels of cell-free DNA, myeloperoxidase-DNA (MPO-DNA), and citrullinated histone H3 (Cit-H3); the latter 2 are specific markers of NETs. Highlighting the potential clinical relevance of these findings, cell-free DNA strongly correlated with acute-phase reactants, including C-reactive protein, D-dimer, and lactate dehydrogenase, as well as absolute neutrophil count. MPO-DNA associated with both cell-free DNA and absolute neutrophil count, while Cit-H3 correlated with platelet levels. Importantly, both cell-free DNA and MPO-DNA were higher in hospitalized patients receiving mechanical ventilation as compared with hospitalized patients breathing room air. Finally, sera from individuals with COVID-19 triggered NET release from control neutrophils in vitro. Future studies should investigate the predictive power of circulating NETs in longitudinal cohorts and determine the extent to which NETs may be novel therapeutic targets in severe COVID-19.
Keywords: Infectious disease; Inflammation; Neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Update of
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps and thrombosis in COVID-19.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 May 5:2020.04.30.20086736. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.30.20086736. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):138999. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.138999. PMID: 32511553 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) as markers of disease severity in COVID-19.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 14:2020.04.09.20059626. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.09.20059626. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):138999. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.138999. PMID: 32511633 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Center for Systems Science and Engineering. Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html Updated May 21, 2020. Accessed May 21, 2020.
-
- doi: 10.1101/2020.03.05.20031906. Song CY, Xu J, He JQ, Lu YQ. COVID-19 early warning score: a multi-parameter screening tool to identify highly suspected patients [preprint]. Posted on medrxiv March 8, 2020. Accessed May 14, 2020. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

