Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Household Contacts of a Healthcare Provider, Wuhan, China
- PMID: 32330112
- PMCID: PMC7392452
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2608.201016
Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Household Contacts of a Healthcare Provider, Wuhan, China
Abstract
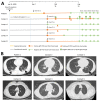
We found that all 5 asymptomatic household contacts of a Wuhan, China, physician with coronavirus disease had severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 detected by PCR. The index patient and 2 contacts also had abnormal chest computed tomography scans. Asymptomatic infected household contacts of healthcare workers with coronavirus disease might be underrecognized.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; China; SARS-CoV-2; Wuhan; asymptomatic; coronavirus disease; healthcare workers; household contacts; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

