Diagnostic accuracy of the iNPH Radscale in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
- PMID: 32330190
- PMCID: PMC7182203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232275
Diagnostic accuracy of the iNPH Radscale in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
Abstract
Background and purpose: The idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) Radscale was developed to standardize the evaluation of radiological signs in iNPH. The purpose of this study was to estimate the diagnostic accuracy of the iNPH Radscale in a sample of "true positive" and "true negative" cases.
Methods: Seventy-five patients with definite iNPH, i.e. who had improved at clinical follow-up one year after ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery, were compared with 55 asymptomatic individuals from the general population. A radiologist assessed the seven radiological features of the iNPH Radscale in computed tomography of the brain in the patients (preoperatively) and controls.
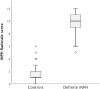
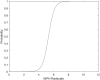
Results: The iNPH Radscale score was significantly higher in the iNPH group (Median = 10, interquartile range 9-11) than in the control group (Median = 1, interquartile range 1-2) (p <0.001). Receiver operated characteristics analysis yielded an area under the curve of 99.7%, and an iNPH Radscale score ≤ 4 identified those without iNPH, with a sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 96% and overall accuracy of 98.5%.
Conclusions: In this study, iNPH Radscale could accurately discriminate between patients with definite iNPH and asymptomatic individuals over 65 years old. According to the results, a diagnosis of iNPH is very likely in patients with an iNPH Radscale score above 8 and corresponding clinical symptoms. On the other hand, the diagnosis should be questioned when the iNPH Radscale score is below the cut-off level of 4. We conclude that the iNPH Radscale could work as a diagnostic screening tool to detect iNPH. Whether the scale also can be used to predict shunt outcome needs further studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

