Ethylene signaling in plants
- PMID: 32332098
- PMCID: PMC7261785
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.010854
Ethylene signaling in plants
Abstract
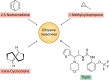
Ethylene is a gaseous phytohormone and the first of this hormone class to be discovered. It is the simplest olefin gas and is biosynthesized by plants to regulate plant development, growth, and stress responses via a well-studied signaling pathway. One of the earliest reported responses to ethylene is the triple response. This response is common in eudicot seedlings grown in the dark and is characterized by reduced growth of the root and hypocotyl, an exaggerated apical hook, and a thickening of the hypocotyl. This proved a useful assay for genetic screens and enabled the identification of many components of the ethylene-signaling pathway. These components include a family of ethylene receptors in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER); a protein kinase, called constitutive triple response 1 (CTR1); an ER-localized transmembrane protein of unknown biochemical activity, called ethylene-insensitive 2 (EIN2); and transcription factors such as EIN3, EIN3-like (EIL), and ethylene response factors (ERFs). These studies led to a linear model, according to which in the absence of ethylene, its cognate receptors signal to CTR1, which inhibits EIN2 and prevents downstream signaling. Ethylene acts as an inverse agonist by inhibiting its receptors, resulting in lower CTR1 activity, which releases EIN2 inhibition. EIN2 alters transcription and translation, leading to most ethylene responses. Although this canonical pathway is the predominant signaling cascade, alternative pathways also affect ethylene responses. This review summarizes our current understanding of ethylene signaling, including these alternative pathways, and discusses how ethylene signaling has been manipulated for agricultural and horticultural applications.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; bioengineering; constitutive triple response 1 (CTR1); ethylene; ethylene-insensitive 2 (EIN2); hormone receptor; phytohormone; plant hormone; signal transduction; signaling.
© 2020 Binder.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
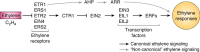
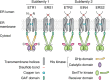

References
-
- Bakshi A., Shemansky J. M., Chang C., and Binder B. M. (2015) History of research on the plant hormone ethylene. J. Plant Growth Regul. 34, 809–827 10.1007/s00344-015-9522-9 - DOI
-
- Abeles F., Morgan P., and Saltveit M. J. (1992) Ethylene in Plant Biology, 2nd Ed., Academic Press, San Diego, CA
-
- Mattoo A. K., and Suttle J. C. (1991) The Plant Hormone Ethylene, CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL
-
- Banks J. A., Nishiyama T., Hasebe M., Bowman J. L., Gribskov M., dePamphilis C., Albert V. A., Aono N., Aoyama T., Ambrose B. A., Ashton N. W., Axtell M. J., Barker E., Barker M. S., Bennetzen J. L., et al. (2011) The Selaginella genome identifies genetic changes associated with the evolution of vascular plants. Science 332, 960–963 10.1126/science.1203810 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rensing S. A., Lang D., Zimmer A. D., Terry A., Salamov A., Shapiro H., Nishiyama T., Perroud P. F., Lindquist E. A., Kamisugi Y., Tanahashi T., Sakakibara K., Fujita T., Oishi K., Shin-I T., et al. (2008) The Physcomitrella genome reveals evolutionary insights into the conquest of land by plants. Science 319, 64–69 10.1126/science.1150646 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

