Recent hemispheric asymmetry in global ocean warming induced by climate change and internal variability
- PMID: 32332758
- PMCID: PMC7181756
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15754-3
Recent hemispheric asymmetry in global ocean warming induced by climate change and internal variability
Abstract
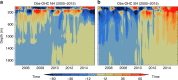
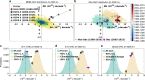
Recent research shows that 90% of the net global ocean heat gain during 2005-2015 was confined to the southern hemisphere with little corresponding heat gain in the northern hemisphere ocean. We propose that this heating pattern of the ocean is driven by anthropogenic climate change and an asymmetric climate variation between the two hemispheres. This asymmetric variation is found in the pre-industrial control simulations from 11 climate models. While both layers (0-700 m and 700-2000 m) experience steady anthropogenic warming, the 0-700 m layer experiences large internal variability, which primarily drives the observed hemispheric asymmetry of global ocean heat gain in 0-2000 m layer. We infer that the rate of global ocean warming is consistent with the climate simulations for this period. However, the observed hemispheric asymmetry in heat gain can be explained by the Earth's internal climate variability without invoking alternate hypotheses, such as asymmetric aerosol loading.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Roemmich D, et al. Unabated planetary warming and its ocean structure since 2006. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015;5:240–245. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2513. - DOI
-
- Wijffels S, Roemmich D, Monselesan D, Church J, Gilson J. Ocean temperatures chronicle the ongoing warming of Earth. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016;6:116–118. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2924. - DOI
-
- Bindoff, N. L. et al. Detection and attribution of climate change: from global to regional. in Climate Change 2013 the Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change vol. 9781107057 867–952 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, 2013).
-
- Bindoff, N. L. et al. Observations: Oceanic Climate Change and Sea Level. in Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change vol. 35 385–432 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, 2007).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

