Current status of potential therapeutic candidates for the COVID-19 crisis
- PMID: 32334062
- PMCID: PMC7175848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.046
Current status of potential therapeutic candidates for the COVID-19 crisis
Abstract
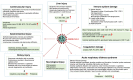
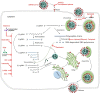
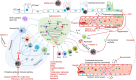
As of April 15, 2020, the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-2019) pandemic has swept through 213 countries and infected more than 1,870,000 individuals, posing an unprecedented threat to international health and the economy. There is currently no specific treatment available for patients with COVID-19 infection. The lessons learned from past management of respiratory viral infections have provided insights into treating COVID-19. Numerous potential therapies, including supportive intervention, immunomodulatory agents, antiviral therapy, and convalescent plasma transfusion, have been tentatively applied in clinical settings. A number of these therapies have provided substantially curative benefits in treating patients with COVID-19 infection. Furthermore, intensive research and clinical trials are underway to assess the efficacy of existing drugs and identify potential therapeutic targets to develop new drugs for treating COVID-19. Herein, we summarize the current potential therapeutic approaches for diseases related to COVID-19 infection and introduce their mechanisms of action, safety, and effectiveness.
Keywords: ACE2 blocker; Antimalaria; Antiviral: Chinese traditional medicine; COVID-19; Immunoenhancer; Monoclonal antibody; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Achiron A. Complications of intravenous gammaglobulin in neuromuscular diseases. Neurology. 1997;49:899–900.
-
- Aggarwal S., Pittenger M.F. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105:1815–1822. - PubMed
-
- Agostini M.L., Andres E.L., Sims A.C., Graham R.L., Sheahan T.P., Lu X., Smith E.C., Case J.B., Feng J.Y., Jordan R., Ray A.S., Cihlar T., Siegel D., Mackman R.L., Clarke M.O., Baric R.S., Denison M.R. Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. mBio. 2018;9:e00221–18. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agostini M.L., Pruijssers A.J., Chappell J.D., Gribble J., Lu X., Andres E.L., Bluemling G.R., Lockwood M.A., Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., Natchus M.G., Saindane M., Kolykhalov A.A., Painter G.R., Baric R.S., Denison M.R. Small-molecule antiviral β-d–hydroxycytidine inhibits a proofreading-intact coronavirus with a high genetic barrier to resistance. J. Virol. 2019;93:e01348–19. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

