Preliminary estimates of the reproduction number of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in Republic of Korea and Italy by 5 March 2020
- PMID: 32334115
- PMCID: PMC7194543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.044
Preliminary estimates of the reproduction number of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in Republic of Korea and Italy by 5 March 2020
Abstract
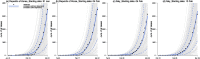
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak has caused 6088 cases and 41 deaths in Republic of Korea, and 3144 cases and 107 death in Italy by 5 March 2020, respectively. We modelled the transmission process in the Republic of Korea and Italy with a stochastic model, and estimated the basic reproduction number R0 as 2.6 (95% CI: 2.3-2.9) or 3.2 (95% CI: 2.9-3.5) in the Republic of Korea, under the assumption that the exponential growth starting on 31 January or 5 February 2020, and 2.6 (95% CI: 2.3-2.9) or 3.3 (95% CI: 3.0-3.6) in Italy, under the assumption that the exponential growth starting on 5 February or 10 February 2020, respectively.
Keywords: Basic reproduction number; COVID-19; Coronavirus disease 2019; Italy; Republic of Korea.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Italian town shows zest for history with ‘Battle of the Oranges’ food fight. Available online: https://abcnews.go.com/International/italian-town-shows-zest-history-bat... [accessed 05.03.20].
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

