Prediction for the spread of COVID-19 in India and effectiveness of preventive measures
- PMID: 32334157
- PMCID: PMC7169890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138762
Prediction for the spread of COVID-19 in India and effectiveness of preventive measures
Abstract
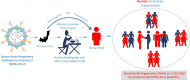
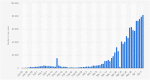
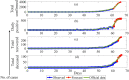
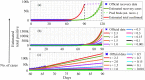
The spread of COVID-19 in the whole world has put the humanity at risk. The resources of some of the largest economies are stressed out due to the large infectivity and transmissibility of this disease. Due to the growing magnitude of number of cases and its subsequent stress on the administration and health professionals, some prediction methods would be required to predict the number of cases in future. In this paper, we have used data-driven estimation methods like long short-term memory (LSTM) and curve fitting for prediction of the number of COVID-19 cases in India 30 days ahead and effect of preventive measures like social isolation and lockdown on the spread of COVID-19. The prediction of various parameters (number of positive cases, number of recovered cases, etc.) obtained by the proposed method is accurate within a certain range and will be a beneficial tool for administrators and health officials.
Keywords: COVID-19; Curve fitting; LSTM; Prediction; Recurrent neural network.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Connor J.T., Martin R.D., Atlas L.E. Recurrent neural networks and robust time series prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994;5(2):240–254. - PubMed
-
- Hochreiter S., Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997;9(8):1735–1780. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W., Schotten H.D. Deep learning for fading channel prediction. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2020;1:320–332. (early access)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

