Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia - A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
- PMID: 32334395
- PMCID: PMC7162793
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.018
Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia - A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Abstract
Background and aims: Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is chronic conditions with devastating multi-systemic complication and may be associated with severe form of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis in order to investigate the association between DM and poor outcome in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.
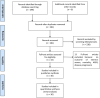
Methods: Systematic literature search was performed from several electronic databases on subjects that assess DM and outcome in COVID-19 pneumonia. The outcome of interest was composite poor outcome, including mortality, severe COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), need for intensive care unit (ICU) care, and disease progression.
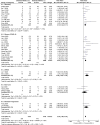
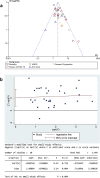
Results: There were a total of 6452 patients from 30 studies. Meta-analysis showed that DM was associated with composite poor outcome (RR 2.38 [1.88, 3.03], p < 0.001; I2: 62%) and its subgroup which comprised of mortality (RR 2.12 [1.44, 3.11], p < 0.001; I2: 72%), severe COVID-19 (RR 2.45 [1.79, 3.35], p < 0.001; I2: 45%), ARDS (RR 4.64 [1.86, 11.58], p = 0.001; I2: 9%), and disease progression (RR 3.31 [1.08, 10.14], p = 0.04; I2: 0%). Meta-regression showed that the association with composite poor outcome was influenced by age (p = 0.003) and hypertension (p < 0.001). Subgroup analysis showed that the association was weaker in studies with median age ≥55 years-old (RR 1.92) compared to <55 years-old (RR 3.48), and in prevalence of hypertension ≥25% (RR 1.93) compared to <25% (RR 3.06). Subgroup analysis on median age <55 years-old and prevalence of hypertension <25% showed strong association (RR 3.33) CONCLUSION: DM was associated with mortality, severe COVID-19, ARDS, and disease progression in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Diabetes mellitus; Mortality; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures

Comment in
-
Diabetes is not associated with COVID-19-related mortality in older institutionalized people.Diabetes Metab. 2021 May;47(3):101235. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2021.101235. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Diabetes Metab. 2021. PMID: 33515718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 and Diabetes: Handle with Care.MEDICC Rev. 2020 Oct;22(4):7. doi: 10.37757/MR2020.V22.N4.16. Epub 2020 Oct 30. MEDICC Rev. 2020. PMID: 34297710 No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: Clinical Course, Metabolic Status, Inflammation, and Coagulation Disorder.Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021;12(5):6-16. doi: 10.17691/stm2020.12.5.01. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021. PMID: 34796000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report – 78.
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

